
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Determine the maximum possible mass (m) in kilograms so that the block will remain in position without slipping .
What is the minimum possible value of mass (m) in kilograms so that the block will remain in position without slipping.
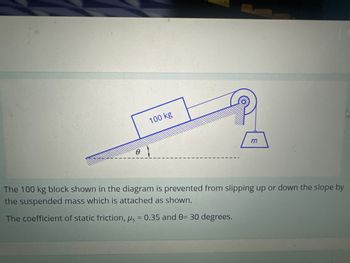
Transcribed Image Text:0
100 kg
P
m
The 100 kg block shown in the diagram is prevented from slipping up or down the slope by
the suspended mass which is attached as shown.
The coefficient of static friction, μs = 0.35 and 0= 30 degrees.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q2. As shown on the right in image below, the force Facting on the box varies with displacement s, and the coefficient in the image, C = 15. Determine the work done by force Fto the box when the box has displaced s = 0.8 m. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Negative sign must be included if the work done is negative. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper Sl unit. F (N) F 3 s – C s (m) 1 2.arrow_forwardThe tensile force of the cable (AB) is 8kN. The effect of the tensile force of the two cables (AB, AC) is notFind the tensile force (T) of the cable (AC) required to make the force act in the directionFind the resultant force (R) acting in the high and downward directions.arrow_forwardA passenger is standing on a scale in an elevator. The building has a height of 500 feet, the passenger has a mass of 80 kg, and the scale has a mass of 7 kg. The scale sits on the floor of the elevator. (It is an Otis elevator, so we will label it as "O" so as not to confuse its forces with those caused by the earth.) You may take g = 10 N/kg. For doing this problem it might be useful to start by drawing free-body diagrams for the passenger and the scale.Consider the vertical forces acting on the passenger and the scale WE→P: The force of the earth pulling down on the passenger (weight). WE→S: The force of the earth pulling down on the scale (weight). NP→S: The force of the passenger pushing down on the scale (normal). NS→P: The force of the scale pushing up on the passenger (normal). NO→S: The force of the elevator pushing up on the scale (normal). NO→P: The force of the elevator pushing up on the passenger (normal) a) While it is accelerating downward, which of the forces in your…arrow_forward
- A block sits on a plane, and there is friction between the block and the plane. The plane is accelerated to the right. If the block remains at the same position on the plane, which of the following pictures might show the free-body diagram for the block? (All of the vectors shown are forces.) N (zero force) Fi та та mg mg mg mgarrow_forwardD) Determine the true magnitude and direction of the forces acting on the cylinderarrow_forwardA dam on a river is built so that the wall facing the water is shaped like the region above the curve y = 0.52 and below the line y = 280. (Here, distances are measured in meters.) The water level is 40 meters below the top of the dam. Find the force (in Newtons) exerted on the dam by water pressure. kg m³ (Water has a density of 1000- and the acceleration of gravity is 9.8- m sec² L 80 SHE GRADEarrow_forward
- Calculate the mass of an object that has a weight of 800 Narrow_forwardBlock 1 (19 kg) is setting on the floor of an elevator. A rope pulls vertically up on block 1 with a tension of 10 N. The elevator is moving downward with a decreasing speed and the magnitude of the acceleration is 2 m/s2.On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component. NET force on Block 1Fnet1 = i + j N FORCES on BLOCK 1Weight force on block 1 by EarthW1E = i + j N Tension Force on block 1 by RopeT1R = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by SurfaceN1S = i + j Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY