
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
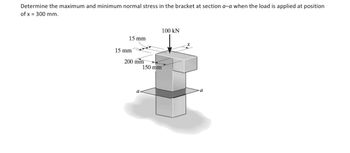
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the maximum and minimum normal stress in the bracket at section a-a when the load is applied at position
of x 300 mm.
15 mm
15 mm
200 mm
150 mm
100 KN
a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The frame supports a centrally applied distributed load of 1.8 kip/ft Determine the state of stress at points A and B on member CD and indicate the results on a volume element located at each of these 12 ft points The pins at C and D are at the same location as the neutral axis for the cross-section A -5 ft E TI 3 in. 3 in. 1 in. B 1.5 in. 6 in. 16 ft 1.8 kip/ft Darrow_forwardF The shaft is loaded with two forces as shown and is fixed at A. The strength is defined as the maximum allowable force F that does not produce shear stress above the material's maximum al- lowable value of 4 ksi. Determine the strength. By what factor would the strength increase if the shaft diameter were doubled? (L₁ = 12 in., L₂ = 6 in., and d = 0.5 in.)arrow_forwardQuestion 2. The hollow steel shaft has a diameter of 65 mm and thickness of 5mm, is subjected to a torque and moment produced by a 3 kN force which is 15 mm from the centre of the shafts cross section. The shafts have the same centroid. a. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal stress, maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress in the at point J and K. b. If the weld has a 30° at point J, what is the maximum shear stress the weld has to with- stand. K 700 mm F=3kN 15 mm c. Determine the maximum bending stress if the hole in the cross section area is now off centre by 2 mm in the x and y direction.arrow_forward
- The W-kg man stands in the position shown. If the center of gravity of the man is at Gand assuming that the contact point at C is smooth.a) Find the reactions at B and C. b) Determine the state of stress at point A on the cross section of the plank at sectiona–a (Cubic stress element in 2D).arrow_forwardThe 3/4-in.-diameter shaft is subjected to the loading shown. Determine the stress components at point A. Sketch the results on a volume element located at this point. The journal bearing at C can exert only force components Cyand Cz on the shaft, and the thrust bearing at D can exert force components Dx, Dy, and Dz on the shaft.arrow_forwardTwo wood members of uniform cross section are joined using a simple glued scarf splice. Determine the normal and shearing stresses in the glued splice. The column is loaded in tension through the centroid with the load indicated. 2.4 kip 6" 60° 2.4 kiparrow_forward
- Determine the maximum ram force P that can be applied to the clamp at D if the allowable normal stress for the material is sallow = 180 MPa.arrow_forwardThe solid 0.85-in.-diameter rod is subjected to a uniform axial distributed loading along its length of w = 500 lb/ft. Two concentrated loads also act on the rod: P = 1900 lb and Q = 900 lb. Assume a = 12 in. and b = 24 in. Determine the normal stress in the rod at the following locations: (a) x = 8 in. (b) x = 24 in.arrow_forward1. The pictured link acts as a part of the elevator control for a small airplane. If the attached aluminum tube has an inner diameter of 25 mm and a wall thickness of 5 mm, determine the shear stress in the outer and inner surfaces of the tube when a cable force of 600 N is applied to the cables. Also, sketch the shear-stress distribution over the cross-section.arrow_forward
- Similar problem already solved on bartleby. Take reference from there.arrow_forwardThe screw of the clamp exerts a compressive force of 250 lb on the wood blocks. The cross section is rectangular, 0.75 in. by 0.50 in 4 in. 0.75 in. a Part A Determine the maximum normal stress along section a- a. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units. HA ? Omax = 52.8 ksiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY