
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
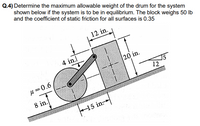
Transcribed Image Text:### Problem Statement:
**Q.4)** Determine the maximum allowable weight of the drum for the system shown below if the system is to be in equilibrium. The block weighs 50 lb and the coefficient of static friction for all surfaces is 0.35.
### Diagram Explanation:
- The system comprises a block and a drum connected by a horizontal bar. The block rests on an inclined plane while the drum is placed at the bottom of the incline.
- Measurements provided in the diagram:
- The block has a height of 20 inches and a width of 12 inches.
- The distance from the bottom-left corner of the block to the center of the drum is 15 inches horizontally.
- The drum has a diameter of 8 inches.
- The rod connecting the drum and the block is 4 inches from the top of the block.
- The incline makes an angle with the horizontal, with a tangent value of \( \frac{5}{12} \).
- Coefficients of friction:
- Between the drum and the plane: \( \mu = 0.6 \)
- Between the block and the plane: \( \mu = 0.35 \)
### Given Data:
- Weight of the block (\( W_b \)): \( 50 \) lbs
- Coefficient of static friction for all surfaces (\( \mu \)): \( 0.35 \)
### Objective:
To determine the maximum allowable weight of the drum (\( W_d \)) to ensure the system remains in equilibrium.
### Key Considerations:
- Analyze forces acting on both the block and the drum.
- Consider frictional forces, normal forces, and gravitational forces to set up equilibrium equations.
- Ensure to account for the incline’s angle in force calculations for both normal and frictional components.
### Solution Approach:
1. *Components of Forces on the Inclined Plane*:
- Resolve the weight of the block and drum into components parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane.
- Consider static friction forces opposing the motion where required.
2. *Equilibrium Conditions*:
- Set up force balance equations in the directions parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane.
- Ensure torque equilibrium around appropriate pivot points where moments are balanced.
By using principles of static equilibrium, solve the resulting equations to find the maximum allowable weight of the drum (\( W_d \)).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 250 lb refrigerator is being pushed. You do not know what force P should be applied. The coefficient of static friction between the refrigerator and floor is lg = 0.4. The center of gravity of the refrigerator is at point G. - d2 -- d2 F1 d3 d1 d4 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value di 4.5 ft d2 1.5 ft d3 2.5 d4 3.5 a. Determine the force P that is needed to overcome friction. b. Determine the location of the normal force r measured from the center of the refrigerator if the force P from part a is applied. c. Determine the minimum force P that is required to tip the refrigerator. d. Will the refrigerator slip or tip first? Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. P= lb ft Pip = lb Will the refrigerator slip or tip first? tip O sliparrow_forwardA chain having a length L and weight W rests on a street for which the coefficient of static friction is us. If a crane is used to hoist the chain, determine the force P it applies to the chain if the length of chain remaining on the ground begins to slip when the horizontal component is Px. What length of chain remains on the ground? Given: L = 20 ft W = 8lb/ft = 0.2 us= : 10 lb Px =arrow_forwardThe coefficient of friction between the 120 lb block (shown in figure below) and the incline plane is 0.3 and that between the cord and cylindrical support is 0.4. Determine the range of cylinder weight W for which the system shown below will be in equilibrium. μ = 0.3 120 lb 24° www. Charice W μ = 0.4arrow_forward
- The high strength, square-threaded bolt that holds the three plates together has a nominal diameter of 1 in. The coefficient of friction is us = 0.36. The mean diameter of the thread is 0.94 in. The lead of the bolt is L = 0.160 in. Neglect friction between the nut and the washer. Determine the torque one must apply in in. Ib to the nut to induce a tension of 47,500 lb. (Enter the magnitude.) in. · Ib When that tension is achieved, determine the torque in in. · Ib required to loosen the bolt. (Enter the magnitude.) in. • Ibarrow_forward7. Draw a free body diagram of the crate. Also, answer the multiple choice question.arrow_forwardDetermine the maximum allowable weight of the drum for the system shown below if the system is to be in equilibrium. The block weighs 60 lb and the coefficient of static friction for all surfaces is 0.4 7" 4" 25 O 9" 13" 18"arrow_forward
- 2. The wedge blocks are used to hold the specimen in a tension testing machine. Determine the design angle 0 of the wedges so that the specimen will not slip regardless of the applied load. The coefficients of static friction are LA at A and l8 at B. Neglect the weight of the blocks. B Given: HA = 0.1 HB = 0.6 %3Darrow_forwardNeed only a handwritten solution only (not a typed one).arrow_forwardThe crate has a weight of W = 350 lb and the %3D coefficient of static Friction between the crate and the ground is µs = 0.3. If the angle %3D e = 45° and P = 100 lb, the normal force 'N' exerted on the crate is. Select one: a. 83.79-lb b. 70.71-lb С. О d. 279.29-lbarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY