
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
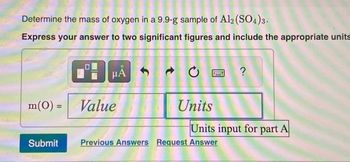
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the mass of oxygen in a 9.9-g sample of Al2(SO4)3.
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units
m(0) =
Submit
HÅ
Value
1
Units
?
Units input for part A
Previous Answers Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A student sets up the following equation to solve a problem in solution stoichiometry. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Enter the units of the student's answer. (0.19 L) 1 mL 10-³ 146.86 g mol 1.04 mL = ☐ x10 ロ・ロ X I 00arrow_forwardGiven the following equation: 8 Fe + Sg → 8 Fes How many moles of iron is needed to react with 16.0 moles of sulfur? Show all of your work and round to the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forward2. A mixture of KCr(SO4)2 and its hydrate KCr(SO4)2-12H₂O has a mass of 1.2843 g. After heating to drive off all the water, the mass is only 1.1079 g. What is the weight percentage of KCr(SO4)2-12H₂O in the original mixture? Report your answer to 4 significant figures. Molar masses: KCr(SO4)2 283.22 g/mol; KCr(SO4)2-12H₂O 499.40 g/mol.arrow_forward
- Solid ammonium chloride,NH4Cl, is formed by the reaction of gaseous ammonia,NH3, and hydrogen chloride, HCl. NH3(g)+HCl(g)⟶NH4Cl(s) A 6.14 g sample of NH3 gas and a 6.14 sample of HCl gas are mixed in a 1.00 L flask a 25 ∘C. Identify the limiting reagent. How many grams of NH4Cl will be formed by this reaction? What is the pressure in atmospheres of the gas remaining in the flask? Ignore the volume of solid NH4Cl produced by the reaction.arrow_forward6 CO2 (g) + 6 H20 (- CH1206 (s) + 6 O2 (g) How many grams of carbon dioxide would be required to produce 42.5 g C,H1206? In the 'Answer' box, express your numerical answer to the nearest ±0.1arrow_forwardAcid rain is caused in part by burning coal that contains sulfur impurities. The sulfur is converted first to SO2, which reacts with oxygen and atmospheric moisture to produce sulfuric acid, H2SO4. If a particular coal contains 1.90% sulfur (by mass), calculate the mass of sulfuric acid produced by burning a metric ton (1000 kg) of the coal.arrow_forward
- A student sets up the following equation to solve a problem in solution stoichiometry. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Enter the units of the student's answer. mol (4.6(0472) (26.16 )= mol 0x10 ロ・ロ X 3 0|0 5arrow_forward7 Sodium azide (Na,N) decomposes on heating to form sodium and nitrogen gas. 2Na,N → 6Na + N2 1.35g of sodium nitride were heated. a Calculate the mass of sodium formed on complete decomposition of the sodium nitride. Give your answer to 3 significant figures. (AO2) 3 marks b Calculate the volume of nitrogen gas (in cm³) produced on complete decomposition of 1.35 g of sodium nitride at 320K and 110kPa. The gas constant R = 8.31JK-'mol-'. Give your answer to 3 significant figures. (AO2) 3 marksarrow_forwardn3 of 14 Phosphorus reacts with oxygen to form diphosphorus pentoxide, P,0,. 4 P(s) + 5 0,(g) - → 2 P,0,(s) How many grams of P,O, are formed when 3.83 g of phosphorus reacts with excess oxygen? Show the unit analysis used for the calculation by placing the correct components into the unit-factor slots. 言 性 料 E 3.83 g P × = g P,O, 自 自 5. 2 .... 雪 Answer Bank 32.00 g O2 141.94 g P2O5 4 mol P 30.97 g P 1 mol P205 2 mol P205 1 mol O, 5 mol O2 1 mol P , , AT- rs .** r a s W, e | | contact us | help about us privacy policy terms of use careers MacBook Airarrow_forward
- O 00 5 Phosphorus reacts with oxygen to form diphosphorus pentoxide, P,O,. 4 P(s) + 50,(g) –→ 2 P,0,(s) How many grams of P,O, are formed when 6.71 g of phosphorus reacts with excess oxygen? Show the unit analysis used for the calculation by placing the correct components into the unit-factor slots. 6.71 g P x = g P,O, Answer Bank 32.00 g 0, 4 mol P I mol P 30.97 g P 2 mol P,O, I mol P,0, I mol O, 141.94 g P,0, 5 mol 0, grams of P,0,: g P,0,arrow_forwardWhen solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of solution according to the equation AGNO3 (aq) + NaCI(aq)→AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) Part A What mass of silver chloride can be produced from 1.69 L of a 0.214 solution of silver nitrate? Express your answer with the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) ? mass of AgCl = Value Units Submit Part B The reaction described in Part A required 3.48 L of sodium chloride. What is the concentration of this sodium chloride solution? Express your answer with the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) HA ? Value Units Submitarrow_forwardAn amount (in grams) of nitrogen gas is reacted with excess hydrogen, according to the balanced reaction shown below. If 104 g of NH3 is recovered, giving a percent yield of 42%, what was the mass of the nitrogen (in grams) that reacted? N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) --> 2 NH3 (g) Report your answer as an integer, that is as a number with zero decimal places, and with no units. Do NOT use scientific notation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY