
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Determine the magnitude of the force that you need to exert on the end of the stick (perpendicular to it) so that the cylinder moves with a constant speed.
Determine the work done by your hand on the stick while your hand makes one full turn around the axis.
Determine the work done by the stick on the cylinder during the one full term around the axis.
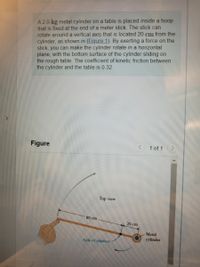
Transcribed Image Text:A 2.0-kg metal cylinder on a table is placed inside a hoop
that is fixed at the end of a meter stick. The stick can
rotate around a vertical axis that is located 20 cm from the
cylinder, as shown in (Figure 1). By exerting a force on the
stick, you can make the cylinder rotate in a horizontal
plane, with the bottom surface of the cylinder sliding on
the rough table. The coefficient of kinetic friction between
the cylinder and the table is 0.32.
Figure
1 of 1
Top view
80 cm
20 cm
Metal
cylınder
Axis of rotation
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- %3D A 3.7-kg sphere is suspended by a cord that passes over a 1.7-kg pulley of radius 3.4 cm. The cord is attached to a spring whose force constant is k = 86 N/m as in the figure below. Assume the pulley is a solid disk. www- (a) If the sphere is released from rest with the spring unstfetched, what distance does the sphere fall through before stopping? 0.3079 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m (b) Find the speed of the sphere after it has fallen 25 cm. 1.67 m/sarrow_forward8. One radian equals approximately Your answer 9. If a 14 kg box is raised to a height of 4.0 m on Earth, what is its gravitational potential energy relative to the ground? Your answer Submit Never submit passwords through Google Forms. This form was created inside of Newport News Public Schools. Report Abusearrow_forwardItem 11 The pulley in (Eigure 1) has radius 0.160 m and moment of inertia 0.380 kg. m². The rope does not slip on the pulley rim. Figure 4.00 kg 5.00 m 2.00 kg 1 of 1 Part A Use energy methods to calculate the speed of the 4.00 kg block just before it strikes the floor. Express your answer with the appropriate units. V= Submit μA Value Request Answer < Return to Assignment Units SWIN Provide Feedback ? 11 of 11 Review | Constantsarrow_forward
- Item 11 The pulley in (Figure 1) has radius 0.160 m and moment of inertia 0.380 kg - m². The rope does not slip on the pulley rim. Figure 4.00 kg 5.00 m 2.00 kg 1 of 1 Part A V = Use energy methods to calculate the speed of the 4.00 kg block just before it strikes the floor. Express your answer with the appropriate units. μÀ Value Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardTwo solid spheres of radius R and mass m are initially separated by a distance d such that the two centres of mass are separated by d+3R as shown below. The spheres are initially at rest, but the gravitational force accelerates them towards each other until they collide.a) Calculate the initial mechanical energy of the system.b) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the system at the moment they collide.c) Derive an expression for v. State carefully what physical law you are applying.d) Show that, in the limit d >> R, the velocity v is independent of d.arrow_forwardA thin cylindrical ring starts from rest at a height h1 = 98 m. The ring has a radius R = 34 cm and a mass M = 4 kg. Part (a) Write an expression for the ring's initial energy at point 1, assuming that the gravitational potential energy at point 3 is zero. Part (b) If the ring rolls (without slipping) all the way to point 2, what is the ring's energy at point 2 in terms of h2 and v2? Part (c) Given h2 = 32 m, what is the velocity of the ring at point 2 in m/s? Part (d) What is the ring's rotational velocity in rad/s? Part (e) After passing point 2 the hill becomes frictionless and the ring's rotational velocity remains constant. What is the linear velocity of the ring at point 3 in m/s?arrow_forward
- Jerry's great grandmother's vitrola plays records at 78 roatations per minute (rpm). Describe what will happen if Jerry starts the vitrola on a friction free table. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardThe turntable in a microwave oven has a moment of inertia of 0.040 kg⋅m2 and is rotating once every 4.4 s . What is its kinetic energy?Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA hollow cylinder (hoop), a solid cylinder (disk), and a solid sphere, each of mass M and radius R, roll down a hill of height h. Rank the objects based on their total kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill. Rank the one with the most energy 1, etc. If two are equal, give them the same ranking. hoop___________ disk_______________sphere_______________Justify your rankingarrow_forward
- Discuss why the differences in peak torque and average power between the two speeds 60 and 180°/sec during extension. Can you relate these differences to the measurements of strength and power? Why? Use the force-velocity curve to answer this question Extension Peak Torque (N/M) Peak Torque (N/M) 60•/sec Flexion 60°/sec 180°/sec 180•/sec s1 160.7 119.2 s1 78.3 75.3 S2 90.8 57.2 S2 49.3 36.7 S3 132 104.9 S3 89.3 68.2 S4 127.1 88.4 S4 58.8 48.1 S5 213.3 151 S5 98.9 72.3 S6 138.2 104.2 S6 61.8 55.7 S7 115.4 84.1 S7 49.2 40.8 S8 117.5 82.1 S8 59.7 40.2 S9 119.5 80 S9 62.3 43.2 s10 113.7 79.9 S10 53.6 38 s11 122.5 89.2 S11 57.6 33.8 Average 132 95 Average 65 50 Extension Average Power (W) Flexion Average Power (W) 60°/sec 180•/sec 60•/sec 180•/sec s1 120.2 202.5 s1 66.9 113.4 S2 80.9 134.8 S2 45.7 77.1 S3 117.5 272.6 S3 74.7 147.3 S4 116.2 192.2 S4 55.1 105.1 S5 130 255 S5 67.3 108.5 S6 118.9 164.2 S6 59.6 114.7 S7 94.1 187.4 S7 47.7 98.9 S8 94.7 128.9 S8 44 55.2 S9 97.3 130.4 S9 48.1 60.6…arrow_forwardA diver makes 2.0 revolutions on the way from a 8.8-m-high platform to the water. Assuming zero initial vertical velocity, find the diver's average angular velocity during a dive. Number i Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON