
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Solve the following problem and SHOW YOUR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS. ILLUSTRATE THE FREE BODY DIAGRAM for better understanding.
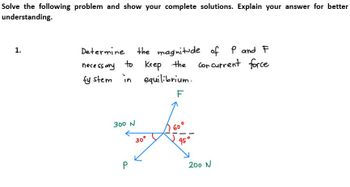
Transcribed Image Text:Solve the following problem and show your complete solutions. Explain your answer for better
understanding.
1.
Determine
necessary
to
sy stem in equilibrium.
F
300 N
the magnitude of P and F
Keep the cor current force
P
30°
S
200 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Only highlighted questions. Please use free body diagrams to explain.arrow_forwardSOLVE THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM AND SHOW YOUR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS. EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWERS FOR BETTER UNDERSTANDING. ILLUSTRATE A FREE BODY DIAGRAM.arrow_forwardPlease draw the free body diagram clear and make sure you show any add forcearrow_forward
- THERE IS NO DIAGRAM IN THE PROBLEM IT IS NOT INCOMPLETE*** Block 1 (16 kg) is located on the surface of a table. A rope pulls on block 1 with a horizontal tension of 113 N to the right and a vertical tension of 150 N upward. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface equals 0.1.On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component.FORCES on BLOCK 1Weight force on block 1 by EarthW1E = i + j NTension force on block 1 by RopeT1R = i + j NNormal force on block 1 by SurfaceN1S = i + j NFrictional force on block 1 by Surfacef1S = i + j N Tries 0/2 What is the acceleration a of block 1?a = i + j m/s2arrow_forwardplease help with b1,b2 and carrow_forwardRefer to the diagram below when answering this question. This question may have more than one correct answer. Sketching a force diagram may help! B A student attaches a string to a wheeled cart and pulls with constant force on the string. There is no friction between the cart and the table. Which of the following describes the motion of the cart while it is pulled with a constant force across the table? The cart O slows down gradually to a stop. O accelerates constantly. O moves at constant speed. 1 3 6 7 8 9. 10 Ne logy.com/common-assessment-delivery/start/5448309818?action=onresume&submissionld=686236351# hp 4-arrow_forward
- Hello, I need help with solving the physics homework. I need to provide a Free Body Diagram and show all work including formulas using. Thanks in advancearrow_forwardA person pushes a box along the ground. The box has the force diagram shown below. Examine the force diagram to answer the following questions: a. Is the box in equilibrium? If so explain how you can tell. If not, explain why not. b. If the person wants the box to move at constant velocity, should they adjust their pushing on the block? If so, explain how they should change their push. If not, explain why they should change nothing about their pusharrow_forwardProblem 14: Using a rope, a man pulls a block of ice across a frozen pond at a constant velocity, as shown in the figure. While they coefficients of static and kinetic friction for ice are low, they are not zero. Consider this problem to involve friction. If necessary, use Fs for the force of static friction, and Fk as the force of kinetic friction. F. Jo Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the block of ice. Add Force O Reset All F 45 X F total,x: + (pos) Ftotal,y: + (pos)arrow_forward
- Block 1 (9 kg) is located on the surface of a table. A hand pushes horizontally to the right on block 1 with a normal force of 108 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface equals 0.8.On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component.FORCES on BLOCK 1Weight force on block 1 by Earth W1E = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by Surface N1S = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by Hand N1H = i + j N Frictional force on block 1 by Surface f1S = i + j N What is the acceleration a of block 1?a = i + j m/s2arrow_forwardConsider the system in the picture below: a cart of mass M with a static friction coefficient u is connected through a massless string to a hanging mass m. M is a capital letter, m is lower case. Write them as such, or vour equations will be confusing, M We want to find the maximum value of the hanging mass m such that the system is in equilibrium. 1. Free body diagram (FBD): Draw a FBD for each: the Cart and the hanging mass. Clearly show all the forces. 2. Clearly write the equilibrium equations for the cart in the horizontal and vertical direction. 3. Clearly write the equilibrium equation for the hanging mass. 4. Solve the system of the three equations above for the hanging mass m. Show your calculation to get credit. 5. What would happen if mass m exceeds this value? Explain.arrow_forwardPlease draw the free diagram clear and also add any forcearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON