
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Determine the force T that will produce impending motion upward of the 500-lb weight in Figure P7–38. (Assume a coefficient of friction of 0.23.) Also find the minimum force T required to hold the 500-lb weight.
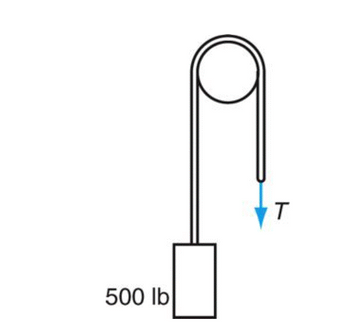
Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding Tension in a Cable and Pulley System
In this diagram, we have a simple pulley system used to analyze the tension force in the cable. Below is a detailed explanation of the depicted components:
**Components of the Diagram:**
1. **Weight Block**: This block represents a weight with a force due to gravity of **500 lb**.
2. **Pulley**: A round, circular object facilitating the change in direction of the cable's tension.
3. **Cable**: The cable runs over the pulley and connects the weight to a tension force denoted as **T**.
**Explanation:**
- The weight box exerts a downward force of **500 lb** due to gravity.
- This force is transmitted through the cable, which passes over a fixed pulley.
- On the right side of the pulley, the tension force in the cable is indicated by the symbol **T**, directing vertically downwards.
**Key Points:**
- The tension **T** in the cable is equal to the weight suspended if the pulley is ideal (frictionless) and the cable is massless.
- Here, the suspended weight is **500 lb**, therefore, the tension **T** in the cable is also **500 lb**.
This scenario illustrates a fundamental principle in mechanics whereby the tension in an ideal pulley system is equal to the weight if the system is in equilibrium, meaning there's no net movement.
Understanding this concept is crucial for solving various problems in physics and engineering related to force, tension, and mechanical advantage in pulley systems.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- draw free body diagram and A and B please. picture is pretty clear! Block is labeled A (under A is 25 degrees) above is 45 degrees and F pulling down is 50 degreesarrow_forwardThe crate shown has a mass of m 20 kg and is being pulled up a plane at 0 25 degrees (to the horizontal) by a cord parallel to the plane, as shown in the following figure: You are given that the coefficient of friction is u = 0.3. State the following: The component of weight parallel to the surface: N. The component of weight perpendicular to the surface: N. The normal reaction: N. The frictional force: N. Calculate the magnitude of the tension, P, in the chord necessary to give an acceleration parallel to the plane of 4 m/s². P is equal to N.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY