
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
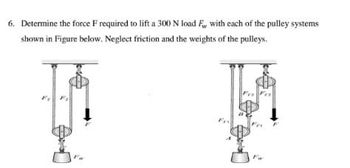
Transcribed Image Text:6. Determine the force F required to lift a 300 N load F, with each of the pulley systems
shown in Figure below. Neglect friction and the weights of the pulleys.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the force obtained in the larger piston of a hydraulic press if 15 N are applied to the smaller one and the circular pistons have four times the radius of each other. Diagram of the problem, necessary formulas, clearance and numerical solutionarrow_forward3 Please help. Provide Free Body Diagram, labeled with appropriate quantities to better understand. Also solve. Thank you.arrow_forwardkindly determine the reaction forcearrow_forward
- NOTE - the reaction force is not shown on the free body diagram you just drew. Do you understand why? Perpendicular and Parallel Forces. A 500 +/- 1 g aluminum block sits in the middle of a balance. Strings with small mass hangers are attached as shown in the diagram. The mass hanger on the right has a total mass of 100 +/- 1 g. The hanger on the left has a mass of 50 +/- 0.5 g. Assume that the balance reads 400.1 +/- 0.1g. 50g Alum. Block Balance 100g As before, follow the procedure in the lab manual to obtain a free body diagram and ultimately the second law equations for the aluminum block. It will be easier if you separate the x and y forces and deal with each direction individually. When you have completed writing the second law equations above, answer the following questions: 2. What is the magnitude of the frictional force acting between the aluminum block and the balance? (You should be able to determine this from your free body diagrams.)arrow_forwardPlease show all work and how you solved it. With proper units and full body diagram if needed, thanksarrow_forwardThe 60 kg two-wheeled cart is described in the figure and parameter table below, with G indicating the location of the center of gravity. It is to be pulled so that it goes up the small step. Find the normal force on each wheel, and the magnitude and direction of the force applied at handle. HINT: remember that there are two wheels sharing the load @080 BY NO SA 2021 Cathy Zupke 4₁1 G L₁ L₂ parameter value 0.6 0.5 0.8 0.7 0.2 A L3 LA d L3 units m m m m m B L₂ F For the answers, take to the right and up to be the positive directions. The normal force at each wheel at A in the x direction is Ax= 150 XN The magnitude of the force at B is F Measured from the positive horizontal axis, the angle of F= 45 X° = 212 XNarrow_forward
- (5) A B $15⁰ 6 in. 100 lb D C E What is the horizontal force on block E applied by the slider D if a = 4 in.? The slider is on wheels and can translate without friction. Draw free body diagrams of ABC and BD.arrow_forwardNeed help. Please round answers to 3 sig figsarrow_forwardWrite down equations for static equilibrium. Calculate the moment about C, and leave the answer in terms of the unknow force of magnitude |FB| After that Caclulate |FB|arrow_forward
- A 68.4 kg man stands on his toes by exerting an upward force through the Achilles tendon, as shown in the figure. Part (a) In units of newtons, what is the magnitude of the force through the Achilles tendon if he stands on one foot? Part (b) Calculate the force in units of newtons at the pivot of the simplified lever system shown. That force is representative of forces in the ankle joint.arrow_forward1. Draw the Free Body Diagrams of pulleys A, B and C and F then using these FBD calculate the force F needed to hold the 1,200-lb force as shown. Assume all the pulleys and ropes to be weightless and ignore the friction between the ropes and pulleys. C B 1,200 lbarrow_forwardGgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY