
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
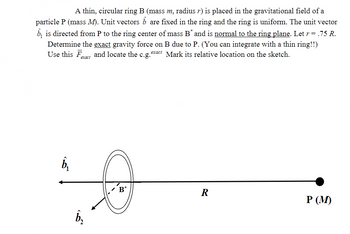
Transcribed Image Text:A thin, circular ring B (mass m, radius r) is placed in the gravitational field of a
particle P (mass M). Unit vectors ô are fixed in the ring and the ring is uniform. The unit vector
bis directed from P to the ring center of mass B* and is normal to the ring plane. Let r = .75 R.
Determine the exact gravity force on B due to P. (You can integrate with a thin ring!!)
Use this F and locate the c.g.exact Mark its relative location on the sketch.
exact
b₂
D
B*
b,
R
P (M)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Draw the small elemental mass dm on the ring and distance x between mass dm and M.
VIEW Step 2: Calculate the mass of small element on the ring in terms of small angle.
VIEW Step 3: Write the gravity force equation between mass dm and mass M.
VIEW Step 4: Integrate the equation for complete circular ring from 0 to 2pi.
VIEW Step 5: Locate the Centre of gravity.
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the gravitational field constant on the surface of the moon is 1.6 N/kg, what is the force of gravity acting on the two objects from 1) if they were on the moon?arrow_forwardA body of mass m is attracted toward a 11.1 kg mass, 31.5 cm away, with a force of magnitude 6.60 10-8 N. Find m. can you also add the units!arrow_forwardA narrow hole is drilled through the centre of a uniform sphere of mass M and radius a. Find the gravitational force exerted on a particle of mass m which is inside the hole at a distance r from the centre.arrow_forward
- A body of mass m is attracted toward a 10.7 kg mass, 27.6 cm away, with a force of magnitude 6.72 x 10-8 N. Find m.arrow_forwardShow complete solution/proceduresarrow_forwardA particle is projected vertically upward in a constant gravitational field with an initial speed Vo. There is a retarding force proportional to the instantaneous speed. Calculate the time it takes to come back to the initial position.arrow_forward
- See attachedarrow_forwardEstimate the gravitational force acting on you?arrow_forwardDetermine the velocity v(t) and position r(t) of a particle of mass m that is projected vertically upwards with initial velocity v, in a uniform gravitational field in a medium with a frictional force proportional to the velocity.arrow_forward
- Assuming the earth to be sphere of uniform mass density, how much would a body weight half way down to the centre of the earth, if it weighted 100 N on the surface.arrow_forward(c) A small object was found to drop above the surface of a big planet with no initial velocity and it fell 13.5 m in 3 s. If the radius of the planet is 5.82 x 10° m, calculate the small object's acceleration during the fall and the mass of the big planet.arrow_forwardImagine that two identical containers, one filled with marbles and the other filled with Styrofoam beads, are released simultaneously from rest from the same height-s Earth's surface. (a) Which container, if either, experiences the greater gravitational force? O the container filled with marbles O the container filled with beads O Both containers will experience the same gravitational force. Justify your answer. O Since both containers fall to the ground with the same acceleration, both will experience the same gravitational force. O Gravitational force is directly proportional to mass, so the heavier container would experience the greater gravitational force. O Gravitational force is inversely proportional to mass, so the lighter container would experience the greater gravitational force. O Since the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s² for each container, both will experience the same gravitational force. (b) which container, if either, experiences the greater acceleration from…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON