
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
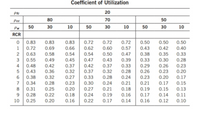
Transcribed Image Text:Coefficient of Utilization
Pfe
20
Pce
80
70
50
Pw
50
30
10
50
30
10
50
30
10
RCR
0.83
0.66
0.83
0.83
0.72
0.72
0.72
0.50
0.50
0.50
0.72
0.69
0.62
0.60
0.57
0.43
0.42
0.40
2
0.63
0.58
0.54
0.54
0.50
0.47
0.38
0.35
0.33
0.55
0.49
0.45
0.47
0.43
0.39
0.33
0.30
0.28
0.42
0.37
0.32
0.28
4
0.48
0.43
0.42
0.37
0.32
0.33
0.29
0.26
0.26
0.23
0.36
0.37
0.28
0.23
0.20
6.
0.38
0.32
0.27
0.33
0.24
0.23
0.20
0.17
7
0.34
0.28
0.23
0.30
0.24
0.21
0.21
0.17
0.15
8.
0.31
0.25
0.20
0.27
0.21
0.18
0.19
0.15
0.13
0.18
0.16
0.28
0.22
0.24
0.19
0.16
0.17
0.14
0.11
10
0.25
0.20
0.22
0.17
0.14
0.16
0.12
0.10

Transcribed Image Text:Determine the coefficient of utilization of an indi-
rect distribution luminaire installed in a 50 ft × 60 ft
room with a 10 ft ceiling height, 30 in. task plane,
and luminaires mounted 2 ft from below the ceiling.
The Pec = 80%, pw = 50%, pje = 20%. Use the
CU table.
How many fixtures are required to maintain 50
foot-candles if the fixtures are two-lamp, 3200 lu-
mens per lamp and LLF is 0.8 based on the product
of LLD and LDD?
ation
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Energy Loss in Bends and Fittings a) What is the difference between major loss and minor losses in a pipe network? Give at least three examples of minor losses? b) The following information has been collected in the lab during "Head Loss in Bends and Fittings" experiment: Manometer readings for sections before and after a bend: h₁=326 mm and h₂=253 mm Q=0.28 lit/s Pipe diameter 1.83 cm Calculate the head loss coefficient (K) for this bend. - c) Name the fitting from the lab experiment (excluding the valve) that should have the highest head loss and explain why this is the case?arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows a pumping system to pump water to an elevated tank. The next page shows the performance curve of a specific type of centrifugal pump. The loss factors at the inlet and outlet are 0.5 and 1.5 respectively while the loss factor associated with the bend is 1.5. The diameter of the pipe is 0.050 m while the total pipe length is 400 m. In order to simplify the calculation you can assume that the friction factor is f= 0.036. Determine the duty point of this pumping system and thus determine the flow rate of the pump for an impeller diameter of 140 mm? Also determine the shaft power of the pump and give an estimate of the pumps efficiency at the duty point. Given that the pump is located 1.80 m above the water surface (1), and the pipe length from inlet to pump is 6.0 m, determine the NPSHA at the pump and state whether cavitation is likely to occur. Sol: 3.6 m 40 H m 30- P 10 20- K₁ = 0.5 5- kW 2- 1- 13 4 2- NPSH K₁ = 1.5 170 160 150 140. 130_ (1) Q 10 Pump 20 54…arrow_forwardAnalysis this graph and explain the relationship between the friction factor and Reynolds numberarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning