
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
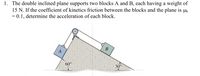
Transcribed Image Text:1. The double inclined plane supports two blocks A and B, each having a weight of
15 N. If the coefficient of kinetics friction between the blocks and the plane is µk
= 0.1, determine the acceleration of each block.
B
A
60°
30°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the minimum force P to prevent the 30-kg rod AB from sliding. The contact surface at B is smooth, whereas the coefficient of static friction between the rod and the wall at A is = 0. - 4m -arrow_forwardThe man pushes on the roller with force P through a handle that connects to the central axle of the roller. If the coefficient of static friction between the 43-lb roller and the floor is Hs = 0.21, and the force Pis maximum so that the roller is about to slip, determine the angular acceleration of the roller (in rad/s?). Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s?. 1.5 ft 30°arrow_forward8 Determine the minimum horizontal force P required to hold the crate from sliding down the plane. The crate has a mass of 100 kg and the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the plane is µ; =0.25 P 30° 9..Determine the minimum force P required to push the crate up the plane. The crate has a mass of 50 kg and the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the plane is us =0.25.arrow_forward
- 2. Two men are sliding a 100-kg crate up an incline. If the lower man pushes horizontally with a force of 500 N and if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.4. determine the tension T which the upper man must exert in the rope to maintain motion of the crate. 30 100 kg 15 = 0.40arrow_forwardA 100 lb crate is initially stationary and is placed along an inclined plane making an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. The coefficients of friction between the crate and the surface are ??=0.2 and ??=0.16. a. If the horizontal force of 90 lb is applied at the crate, determine how far the crate moves from its initial position in 2 sec. b. Determine the acceleration of the block c. If the horizontal force applied to the crate is only 30 lb., how far will the crate moves from its initial position in 2 secs.arrow_forwardThe coefficient of static friction between the 50-kg crate and the ramp is μs = 0.35. The unstretched length of the spring is 800 mm, and the spring constant is k = 660 N/m. Determine the following: 1 The normal force acting on the crate is Blank 1 N. 2 The friction force acting on the crate is Blank 2 N. 3 The minimum value of x at which the crate can remain stationary on the ramp is Blank 3 mm.arrow_forward
- The two 200-lb blocks are pushed apart by the 15° wedge of negligible weight. The angle of static friction is 12° at all contact surfaces. Determine the force P (in pounds, round-off to 2 decimal places) required to start the blocks moving. 15 15 200 lb 200 lbarrow_forwardThe crate in Figure 3.7 has a mass 350 kg and is subjected to a towing force P acting at an angle θ1 = 20° with the horizontal. If the coefficient of static friction is 5, determine the magnitude of P to just start the crate moving down the plane. θ2 = 10° answer=986.61Narrow_forwardIf 7 =200N. determine the friction developed between the S0-kg crate and the ground. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the ground is i, = 0.3.arrow_forward
- Blocks A and B weigh 50 Ib and 30 lb, respectively. Using the coefficients of static friction indicated, determine the greatest weight of block E without causing motion.arrow_forward3. Car A has a mass of 1.4 Mg with center of gravity at point G as shown in Fig. 3. If car B exert a 2 kN, determine whether the force is sufficient to move car A. The static and dynamic friction coefficients between tyre and the road are μ, = 0,5 and μ = 0,35. Assume the surface of car B bumper to be frictionless. 0.5 m 0.8 m 0.8 mi 2 kN 0.4 m Gambar 3. Tyre-Road frictionarrow_forwardDetermine the force P required to force the 15° wedge under the 95-kg uniform crate which rests against the small stop at A. The coefficient of friction for all surfaces is 0.36.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY