
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Determine
a. Cash collection schedule

Transcribed Image Text:Estimated unit sales for the first quarter of 2021 is 40,000 units and expected to increase 10% quarterly. Selling
price fluctuates as follows:
1.
Quarter
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
Unit price
64
66
62
62
Assume that of each quarter's sales: 20% are cash sales while the remaining 80% are credit sales. Shrek & Fiona
Company estimates that 60% of credit sales are collected in the quarter of sale with 2% discount, 30% in the quarter
of following sale, 9% in the second quarter following sale and 1% are considered as uncollectible.
2. Finished product requires 3 pounds of direct materials at P2.50 per pound. Finished good ending inventory is
equal to 10% of the next quarter sales while raw materials ending inventory is equal to 10% of the next quarter
production needs of materials. First quarter of 2022 sales is expected to be at 50,000 units while raw materials
ending is at 13,500 pounds. (Units are rounded to the nearest ones.)
3. Each quarter's purchase are paid 50% in that quarter with 5% purchase discount, 25% in the following quarter
and the remainder in the second quarter following the purchase.
4. Each finished goods requires 5 direct labor hours with an hourly rate of P4.00 payable on the end of each
month.
5. For Factory overhead budget, use the following cost formula:
Indirect labor
PO.02 per direct labor worked (same payment scheme with direct labor)
P2 per unit produced
P48,000 annually, paid at the beginning of the year
Indirect material
Insurance
Factory rent
P6,500 per month
Utilities
P500 per quarter plus PO.50 per unit produced
P300 per quarter plus PO.30 per unit produced
10% of the PPE cost, annually
Maintenance
Depreciation
All overhead costs involve cash outlays are paid in the period which they are incurred, insurance cost. Worthy to
note, the company assumes that all indirect materials are used and paid in the month it was purchased.
6. Selling and administrative expenses
Advertising
P65,000 annually, paid at the beginning of the year
5% of total sales, paid quarterly
Commission
Admin salaries
P100,000 per quarter (same payment scheme with direct labor)
Office rent
P5,000 per month
7. Income tax is 30%, paid on the first quarter of the following year.
8. For cash budget, assume the following:
a. The company desires to maintain P15,000 minimum cash balance
b. Dividend is declared every end of the 4 quarter of the year P15 per issued and outstanding share and paid
every 2 quarter of the following year
c. At the end of the 2 quarter, the company plans to purchase P100,000 worth of equipment.
d. Any excess cash at the end of the 1" quarter of the year is used to buy long term investments P10,000
increments. 3% interest rate is credited to the company's bank account at the quarter's end based on
original cost of investment
e. In case of deficit, the company borrow from the bank P10,000 increments, payable in one year, 10% interest
rate is automatically debited to the company's bank account at the end of every quarter.
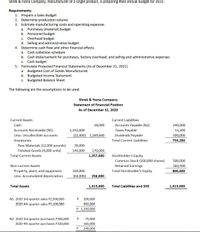
Transcribed Image Text:Shrek & Fiona Company, manufacturer of a single product, is preparing their annual budget for 2021:
Requirements:
1. Prepare a Sales Budget
2. Determine production volume
3. Estimate manufacturing costs and operating expenses
a. Purchases (material) budget
b. Personnel budget
c Overhead budget
d. Selling and administrative budget
4. Determine cash flow and other financial effects
a. Cash collection schedule
b. Cash disbursement for purchases, factory overhead, and selling and administrative expenses
. Cash budget
5. Formulate Projected Financial Statements (As of December 31, 2021)
a. Budgeted Cost of Goods Manufactured
b. Budgeted Income Statement
C. Budgeted Balance Sheet
The following are the assumptions to be used:
Shrek & Fiona Company
Statement of Financial Position
As of December 31, 2020
Current Assets
Current Liabilities
Cash
18,000
Accounts Payable (N2)
240,000
Accounts Receivable (N1)
1,192,000
Taxes Payable
13,200
Less: Uncollectible accounts
(22,400) 1,169,600
Dividends Payable
500,000
Inventories
Total Current Liabilities
753,200
Raw Materials (12,000 pounds)
30,000
Finished Goods (4,000 units)
140,000
170,000
1,357,600
Total Current Assets
Stockholder's Equity
Common Stock (100,000 shares)
Retained Earnings
500,000
Non-current Assets
360,400
Property, plant, and equipment
320,000
Total Stockholder's Equity
860,400
Less: Accumulated depreciation
(64,000)
256,000
Total Assets
1,613,600
Total Liabilities and SHE
1,613,600
N1 2020 3rd quarter sales P2,500,000
200,000
2020 dth quarter sales P3,100,000
992,000
P 1,192,000
N2 2020 3rd quarter purchases P300,000
P
75,000
2020 4th quarter purchases P330,000
165,000
P
240,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education