
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
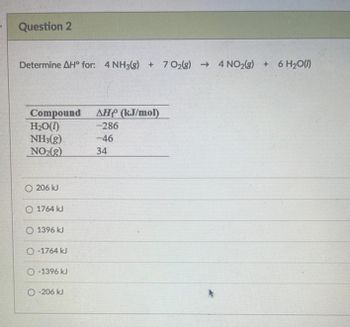
Transcribed Image Text:Question 2
Determine AH° for: 4 NH3(g) + 70₂(g) → 4NO₂(g) + 6 H₂O(1)
Compound
H₂O(1)
NH3(g)
NO₂(g)
O 206 kJ
O 1764 kJ
O 1396 kJ
O-1764 kJ
O-1396 kJ
O-206 kJ
AH (kJ/mol)
-286
-46
34
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- what is the density in g/L (STP) of SO2?arrow_forward1.How many liters does 194.82 grams of CBr4 occupy at STP? 2.How much energy in kJ is released when 11.23 g of aluminum react with an excess of copper oxide? 3 CuO + 2 Al -> 3 Cu + Al2O3 △ H = 1190 kJ/molarrow_forwardCan sodium nitrite form H-bonds with water?arrow_forward
- Does NaCl(s) conduct electricity at room temperature? Yes/No and Explain why?arrow_forwardUsing the values of AG;º from the tables in Appendix C in the back of the textbook, calculate AGº for the following reaction. 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)arrow_forwardThe airbags that protect people in car crashes are inflated by the extremely rapid decomposition of sodium azide, which produces large volumes of nitrogen gas. 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid sodium azide (NaN) into solid sodium and gaseous dinitrogen. 2. Suppose 84.0 L of dinitrogen gas are produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 19.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of sodium azide that must have reacted. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 미미arrow_forward
- b If [OH ] 2.9 x 10¬10 M then РОНarrow_forward18. (a) Molecule N₂H4 (1) + 2 H₂O2 (1) → N2(g) + 4 H₂O (1) Complete the following table: Lewis Dot Structure (use dots or lines to show bonds) (b) (c) (d) N₂H4 H₂O2 N₂ H₂O Calculate the AH°rxn using average bond energies (Table 9.4 in textbook) Calculate the AH°rxn using the standard enthalpies of formation (Appendix 2 in textbook) Why are these two values slightly different?arrow_forwardIn liquid ammonia, NaH and NH3 react to form sodamide (NaNH2). What happens when NaNH2 is placed in water? Use at least one balanced chemical equation in your explanation.arrow_forward
- Upon heating 134 g MgSO4 · 7 H2O:(a) how many grams of water can be obtained? (b) how many grams of anhydrous compound can be obtained?arrow_forwardThe airbags that protect people in car crashes are inflated by the extremely rapid decomposition of sodium azide, which produces large volumes of nitrogen gas. 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid sodium azide (NaN) into solid sodium and gaseous dinitrogen. dlo 2. Suppose 12.0 L of dinitrogen gas are produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 13.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of sodium azide that must have reacted. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Explanation Check O 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use| Privacy | Accessibility > Activity Details You have viewed this topic MacBook Air 4) DI DD F10 F11 F9 F2 F3 F4 F1 10 #3 $ & 3. 4. 6. 8 9.arrow_forwardDoes it make sense that LiH is more stable than other Group 1 hydride compounds? (Choose the best answer.) YES - Lithium has the least covalent character of any of the Group 1 metals. YES - Li+ is the smallest (hardest) of the Group 1 cations and hydride is a small (hard) anion. NO - Lithium has a very high density compared to other Group 1 metals. NO - Because of their similar sizes, Li+ and hydride ions should not interact very strongly.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY