
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Design a spherical tank, with a wall thickness of 2 cm that will assure that no
more than 50 kg of hydrogen will be lost per year. The tank, which will operate
at 500 °C, can be made of nickel, aluminum, copper, or iron. The diffusion
coefficient of hydrogen and the cost per kg for each available material is listed
here.
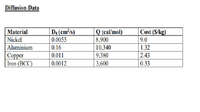
Transcribed Image Text:Diffusion Data
Do (cm/s)
Cost (S/kg)
Q (cal/mol)
8,900
10,340
| 9,380
3,600
Material
Nickel
0.0055
9.0
Aluminium
0.16
1.32
Сорper
Iron (BCC)
0.011
2.43
0.0012
0.33
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cylindrical container is being designed to contain an exothermic chemical reaction. The container has an external diameter of 80 mm and is 0.2 m tall. The temperature of the cylinder must not exceed 500 °C. To improve cooling of the container, fins of thickness t=5 mm and length L= 40 mm are spaced at least 10 mm apart. Each fin has an efficiency of n= 40%. The ambient temperature is maintained at 22 °c and the heat transfer coefficient between the ambient air and the cylinder is 50 W/m2K. If the chemical reaction produces a maximum of 3.2 kW per kilogram of substance, the maximum mass of substance which can safely be processed in the container to 2 decimal places is kg. The effectiveness of each fin to 1 decimal place is You may neglect heat transfer from the tips of the fins and from the circular surfaces of the cylinder.arrow_forwarda piece of beef steak 7 cm thick will be frozen in the freezer room -40 degrees Celsius This product has a moisture content of 73% density 970 kg / m³ and a thermal conductivity of 1.1 W / (m K) frozen using the plank equation. This product has an initial freezing temperature of -1.75 degrees Celsius and the movement of air in the raw chamber gives a convection heat transfer coefficient of 10 W / (m² K). tf =arrow_forwardA food product wants to be produced in a small round shape (pellet) by freezing it in a water blast freezer freezer. Air freezer operates at -30 ° C. The initial product temperature is 25 ° C. The pellet has a diameter of 1 cm, and a density of 980 kg / m³. The initial freezing temperature is -2.5 ° C. The latent heat of freezing of the product is 280 kJ / kg. The thermal conductivity of the frozen product is 1.9 W / (m ° C). The convective heat transfer coefficient is 40 W / (m² K). Calculate the freeze time. t f = Answerhour.arrow_forward
- A food product wants to be produced in a small round shape (pellet) by freezing it in a water blast freezer freezer. Air freezer operates at -25 ° C. The initial product temperature is 25 ° C. The pellet has a diameter of 1.2 cm, and a density of 980 kg / m³. The initial freezing temperature is -2.5 ° C. The latent heat of freezing of the product is 280 kJ / kg. The thermal conductivity of the frozen product is 1.9 W / (m ° C). The convective heat transfer coefficient is 50 W / (m² K). Calculate the freeze time. t f = hour.arrow_forwardA 15 cm (schedule 80, IPS) steam main has a 10 cm thick 'preformed' mineral fibre insulation on it. The thermal conductivity of the insulation is 0.035 W/m °C, and the heat transfer coefficient at the outer surface of the insulation is 10 W/m² °C. What is the critical insulation thickness?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The