
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Derive the equation of internal torques of section AB, i.e. torque for brass sleeve Tb and torque for steel shaft Ts in terms of T using the compatibility equation.
[Note: Please include the matric number and corresponding Gs value.]
![A composite shaft consists of a brass sleeve securely bonded to half steel shaft, fixed at end
A as shown in Figure 1. The brass sleeve and steel shaft have a modulus rigidity Gs = 40
GPa and G. = x0 GPa. The length of the assembly is L = 400 mm. The outer diameters of
the shaft and sleeve are di = 70 mm and d = 90 mm, respectively. Given the shear stress of
brass is th= 70 MPa and shear stress of steel is t,= 110 MPa.
[Note: x value - Use the last non-zero digit from your matric number. If the number is zero,
use the second last digit instead. For example, if your matric number is B051810204, your
x value is 4 and G, = 40 GPa; if your matric number is B051810090, your x value is 9 and
G, = 90 GPa.]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/540793eb-a56b-4b09-8afa-5310c0bfd224/d225369d-e5e9-4b9c-9999-ce842be0d2c3/2fgetpr_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:A composite shaft consists of a brass sleeve securely bonded to half steel shaft, fixed at end
A as shown in Figure 1. The brass sleeve and steel shaft have a modulus rigidity Gs = 40
GPa and G. = x0 GPa. The length of the assembly is L = 400 mm. The outer diameters of
the shaft and sleeve are di = 70 mm and d = 90 mm, respectively. Given the shear stress of
brass is th= 70 MPa and shear stress of steel is t,= 110 MPa.
[Note: x value - Use the last non-zero digit from your matric number. If the number is zero,
use the second last digit instead. For example, if your matric number is B051810204, your
x value is 4 and G, = 40 GPa; if your matric number is B051810090, your x value is 9 and
G, = 90 GPa.]
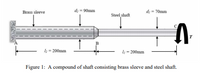
Transcribed Image Text:Brass sleeve
d: = 90mm
di = 70mm
Steel shaft
T
B
I = 200mm
I- 200mm
Figure 1: A compound of shaft consisting brass sleeve and steel shaft.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the Finishing Mill of a hot strip mill, the input shaft of several different gearboxes are each driven by a DC motor of 10,500 HP operating at 125 RPM. For your ASSIGNED gearbox only, you are required to analyze the gearbox capabilities by doing thefollowing: 1. Calculate the maximum motor torque2. calculate the force transmitted by the gearing.3. Using statics, calculate the equivalent radial load at the bearings for BOTH the pinion shaft and the gear shaft. (Four bearings total; two per shaft). Include FBDs of the shafts.4. Research the load capacities for the bearings.(Hint: the bearing manufacturer is most likely Timken / Torrington).5. Calculate the expected bearing life for each bearing.6. Calculate the safety factor for both the bending strength and the pitting resistance for the pinion shaft AND the gear shaft gear teeth based on the transmitted load and the gear material(s).7. Draw the shear, bending moment, and torque diagrams for the GEAR SHAFT ONLY.8. Calculate the…arrow_forwardOh no! The bearing at the wall on the left has been damaged. It is now acting like another gear that can resist a moment(TW). You estimate the shaft has had torsional loading as follows: TA= 200 Nm TB= 530 Nm TC= 120 Nm TD= 150 Nm TW =? See the diagram for the direction of the torques on the shaft. The shaft diameter is 60 mm. The shaft looks ok but you are checking to see if it has exceeded the allowed shear stress for the shaft. Tw .600 mm 600 mm 600 mm A) Which segment has the maximum Torsion? B) What is the maximum shear stress due to torsion? C) Assume Tallow = 60 MPa did the shaft exceed the allowed shear?arrow_forwardPlease full steps. Big clear Handwriting. Thanksarrow_forward
- Please answer part a and barrow_forwardImagine two gears in mesh, the pinion is rotating clockwise, what is the force analysis for such a gear ( draw FBD) with full explanation. For another case: two gears in mesh and the gear is rotating clockwise also draw FBD and with explanations for the direction of rotation of pinion and direction of the resultant forces.arrow_forward1.Please design a pair of spur gears in the milling machine. It is known that power input is 7.5kW, Ni 1450r /min, and the %3D transmission ratio is required to be u = 2.08. F1. If there is slight impact, the supplementary conditions for trial design of this pair of gears: primary selection k = 1.8, number of smaller gear teeth Z1 = 26. The allowable stress and factors for material %3D is: [0]= 600 MPa, [o„]z= 599 MPa, [0,]ı= 220 MPa, [0,]= 213 MPa. E=1.693, Z, =1898/mpa Z„ = 2.5 K =1.25 Ky =1.1 K K =1.2 На K =1.35 Y =2.65, Y = 2.28 Y =1.58 Y =1.76 %3D Fa2 Fal sa1arrow_forward
- (4) An electric motor purchased by your employer surprisingly arrived without a keyway in the shaft. The motor has power rating of 7.5kW & 1,800rpm & has a shaft of Ø17mm. It will be used to drive a centrifugal pump using cast iron sheave. Design the square key to be used in the assembly based on maximum bearing & shearing stresses of 580MPa & 370MPa, respectively, and factor of safety of 5.arrow_forwardA gear drive is required to transmit a maximum power of 22.5KW, the velocity ratio is 1:2 and the rpm of the pinion is 200 .the approximate center distance between the shaft may be taken as 600mm.the teeth has 20°stub involute profile.the static stress for the gear material ( which is cast iron ) may be taken as 60MPa and face width as 10 times the module.find the module, face width and number of teeth on each gear.Check the design for dynamic and wear loads. The deformation factor in the buckling equation may be taken as 80 and material combination factor for the wear as 1.4arrow_forwardHi, I need help with this question.arrow_forward
- A motor is used to drive a gear assembly at 200 rpm. The main gear is in the center of a 1 m long (0.5 m to the left and right of the gear) 50 mm diameter solid circular shaft, and power is taken from the two shaft ends. 25 kW is taken on the left end and an unknown amount of power is taken at the right end. the torque to the left side of the gear is? maximum shear stress to left of gear? If the maximum shear stress on the shaft to the right of the gear is 125 MPa, approximately how much power is being drawn off from the right side of the shaft? The shaft can be made from 6061-T6 aluminum. It has adequate strength to withstand the loading conditions in the scenario, including the loading on the right side of the shaft. true or false?arrow_forwardpls expalin to me step by step and write clearly. i will rate your answer immediately thanksarrow_forwardO d. 25T Nm QUESTION 17 A stepped shaft subjected to a uniform torque T along its length is shown in the figure. When D = 2d, the angle of twist per unit length (0/L) of smaller diameter segment is, %3D O a. equal to that of larger diameter segment. Ob. twice that of larger diameter segment. OC.4 times (i.e. 22) that of larger diameter segment. O c. O d. 16 times (i.e. 24) that of larger diameter segment.. QUESTION 18arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY