
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
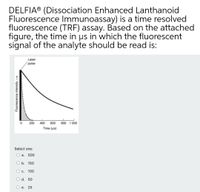
Transcribed Image Text:DELFIA® (Dissociation Enhanced Lanthanoid
Fluorescence Immunoassay) is a time resolved
fluorescence (TRF) assay. Based on the attached
figure, the time in us in which the fluorescent
signal of the analyte should be read is:
Laser
pulse
200
400
600
800 1 000
Time (us)
Select one:
О а. 500
O b. 150
О с. 100
O d. 50
O e. 25
Fluorescence intensity
-------
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Here is the protocol for a UV-Vis spectrophotometer to detect water and chlorine-carbon. 1.Dissolve the water and chlorine-carbon compounds in a solvent, such as water. 2.Prepare a standard solution of known concentration that is similar to the sample being measured. 3.Calibrate the spectrophotometer using the standard solution. 4.Measure the absorbance of the sample using the spectrophotometer. 5.Calculate the concentration of the compounds in the sample using the calibration curve obtained from the standard solution. How is the spectrophotometer calibrated with standard solutions? When is the blank solution placed in the spectrophotmeter?arrow_forwardNAME: LAB SECTION: EXPERIMENT 21: Spectroscopy of Dyes POSTLAB EXERCISE 1. AUV/V is a spectrometer used to measure the absorbance of a solution of hemoglobin bound to oxy- gen at 590 nm. The molar absorptivity was determined to be 8.57 × 104 M-'cm-. The cuvette used had a 1.00-cm sample pathlength. The measured absorbance was ), 140. What was the concentra- tion of hemoglobin in the solution? 2. What would be the absorbance of the solution in question 1 if the pathlength were 2.00 cm? nohntooote 196arrow_forwardA pH probe has a range of 2 to 10 pH units, and a transmitter converts the pH units into a 4 to 20 mA signal. (a) What are the zero and span for the probe? (b) Determine the gain of the probe/transmitter unit. (c) Determine the transmitter output if the pH of a solution is 5.0. (d) If the transmitter gives a reading of 11 mA, what is the pH of the solution?arrow_forward
- What is ln(A) be with reference to ln(A) vs. time graph? What would 1/A be with reference to 1/A vs. time. graph? Trial 1 Time (s) Absorbance 0 0.600 30 0.522 60 0.454 90 0.392 120 0.344 150 0.300 180 0.261arrow_forwardGiven the following size frequency for a dust: Size Interval (um) 7-17.5 17.5-21 21-25 25-28 28-30 30-33 33-36 36-41 41-49 49-70 % by Number 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 a. Plot the cumulative frequency distributions (in %) of the number, surface area, and mass on linear graph paper assuming all particles are spheres with Pp 1.6 g cm ³. = b. Is this a log-normally distributed dust?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- please quickly ,within 1hour thanks ! If it takes longer than an hour, i don't need the answer (1) List the detectors ofHPLC. Describe the advantage and disadvantage for two wideused detectorsarrow_forwardPlease find the absorbance and plot te calibration curvearrow_forwardThe students conducted the assay for LDH activity using the two serum samples. Each cuvette (path length 1 cm) contained 3ml of a suitable assay buffer (including pyruvate as substrate). 20 microlitres of either serum was added to the cuvette and the absorbance values immediately recorded at the optimum wavelength for a period of 5 minutes (absorbance readings taken every 30 seconds). Protein concentration of serum sample (mg/ml) Change in absorbance at optimum wavelength per minute Control serum (C) 8 -0.04 Diseased serum (D) 7.8 -0.6 1c. Using the molar absorption coefficient of NADH as 6220 M-1 cm-1, and by application of the Beer-Lambert law, estimate the enzyme activity in the two samples (C and D). Express activity as moles per second. 1d. Estimate the specific activity of the two samples (moles per second per microgram).arrow_forward
- Three factors were studied: reactor length, carrier flow rate, and sample volume, with the high and low values summarized in the following table. factor high (+1) level low (–1) level X: reactor length 1.3 cm 2.0 cm Y: carrier flow rate 1.6 mL/min 2.2 mL/min Z: sample volume 100 μL 150μL The authors determined the optimum response based on the greatest sensitivity, as determined by the change in potential for the potentiometric detector. The following table summarizes their optimization results. run X* Y* Z* ΔE (mV) 1 –1 –1 –1 37.45 2 +1 –1 –1 31.70 3 –1 +1 –1 32.10 4 +1 +1 –1 27.30 5 –1 –1 +1 39.85 6 +1 –1 +1 32.85 7 –1 +1 +1 35.00 8 +1 +1 +1 32.15 Which factor has the greatest effect on sensitivity (change in potential at the detector)? Which set of conditions optimizes the detection sensitivity?arrow_forwardAnalyte in an unknown gave a signal of 9.3 mV. When 100 mL of 0.211 M standard was added to 100.0 mL of unknown, the signal increased to 16.7 mV. Find the concentration of the original unknown solution.arrow_forwardA solution of a dye was analyzed by spectrophotometry, and the following calibration data were collected using a 1 cm cuvette. *graph in attachemnt* Using the calibration data above for the dye solution, what is the dye concentration in a solution with an absorbance (A) = 0.52 if it was measured in a 1 cm cuvette? Group of answer choices 3.0 x 10-6 M 6.0 x 104 M 2.0 x 10-6 M Not enough information is provided.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY