
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134463216
Author: Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
I have questions about linear patterns.
I know that there has to be a constant change between the variables but how can I find the next variable with given variables if they don’t look constant, and how can I prove they are not linear ?
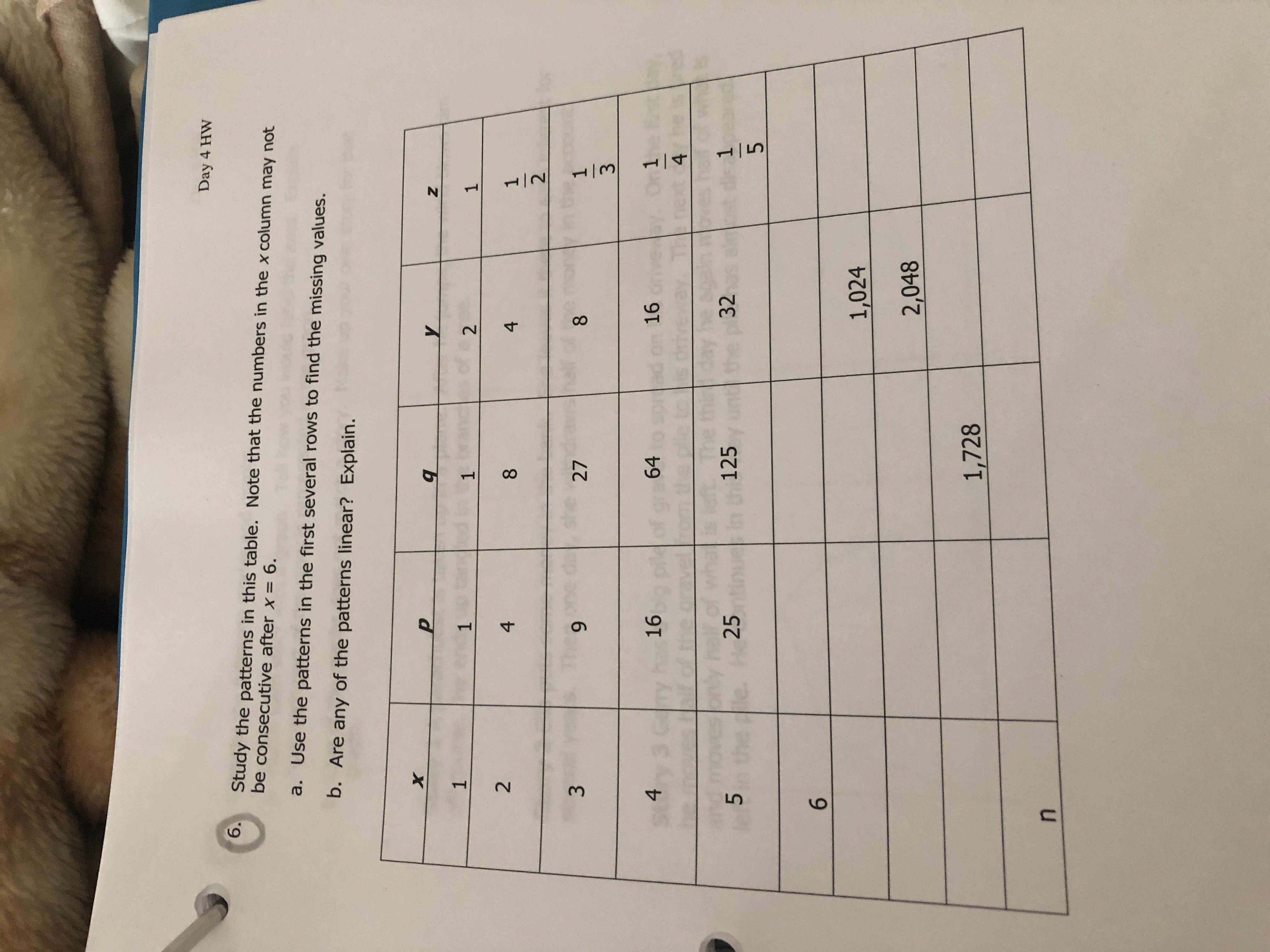
Transcribed Image Text:Day 4 HW
6.
Study the patterns in this table. Note that the numbers in the x column may not
be consecutive after x 6.
a. Use the patterns in the first several rows to find the missing values.
b. Are any of the patterns linear? Explain.
X
Y
1
1
1
2
1
2
4
8
4
1
2
she
3
27
9
8
1
3
43
On1
16
64
16
4
is
1
32
125
25
5
he ple
5
6
1,024
2,048
1,728
LO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the equation for the regression line is y = 6x + 4, then a value of x = –3 will result in a predicted value for y of -14 6 -6 4arrow_forward7. Four students write equations. Do Now-5/7/21 Student 1 y=-5 Student 2 y=- -+21 14-x Student 3 y = Student 4 -8+7 y = Which student writes the equation of a linear function? A Student 1 B Student 2 C Student 3 D Student 4arrow_forwardFlying twice as farA flight from Los Angeles to ABQ is about 2 hours but is 670.2 miles.A flight from San Jose to Chicago is 4 hours but is 1859.0 miles.Can anyone explain why the travel time from San Jose to Chicago is notlonger and closer to 5.75 hours?If the distance increase by 2, shouldnt the time increase by a factorof 2 as well?1. Write a linear model for this question. Takeoff and landing will take a fixed amount of time. Actualtravel in the air will take time proportional to the distance traveled. Think about which of thevariables (time and distance) is the independent variable, and identify the slope and intercept withtheir units.2. Use the data in the quotation to estimate the two constants in your linear model.arrow_forward
- An employee has two options for positions in a large corporation. One position pays $12.20 per hour plus an additional unit rate of $0.80 per unit produced. The other pays $10.40 per hour plus a unit rate of $1.10. (a) Find linear equations for the hourly wages W in terms of x, the number of units produced per hour, for each option. option 1 W1 = option 2 W2 = (b) Use a graphing utility to graph the linear equations and find the point of intersection.(x, y) = ( )arrow_forwardI need help with this problemarrow_forwardSolve only a and b manually using formulas. Show complete solution.arrow_forward
- Put the following steps, for finding a linear model for a set of data using a TI-84 calculator, in the correct order. 1 [Choose] [Choose] Enter your data in STAT-->EDIT with inputs in L1 and outputs in L2 Press STAT-->CALC to access the menu of possible models. Read off your answer, being careful to match the slope to the coefficient of x. Be sure XList: L1, YList: L2, Freg List: (empty) and select "Calculate" Choose LinReg(ax+b) or LinReg(a+bx) [Choose] 3. 4. [Choose] [Choose ]arrow_forwardI need help with this problemarrow_forwardFind the linear curve fit coefficients. Use equations (4a) and (4b) to find these coefficients and determine the units of the coefficients, c1 and c2. Note that the units for these coefficients will not be the same in our two cases. Further note that the calibration coefficients are intermediate quantities, not final results. It is probably best to keep them to four significant digits to avoid round-off errors in subsequent calculations. Lastly, plot the line representing the curve fit. It should appear as a best fit, if you’ve done everything correctly. n is the number of data pairs in the curve-fit. the yi ’s arethe ordinate values (the less precisely known). the xi ’s are the abscissa values (the more precisely known).arrow_forward
- (b) A company manufactures two products, A and B. Each unit of A requires 3 labor hours and each unit of B requires 5 labor hours. Daily manufacturing capacity is 150 labor hours. i) If x units of Product A and y units of product B are manufactured each and all labor hours are to be used, determine the linear equation that requires the use of 150 labor hours per day. How many units of A can be made each day if 25 units of B are manufactured each day? How many units of A can be made each week if 12 units of B are manufactured each day? (Assume a 5-day work week.)arrow_forward3. You have the information that the number of cases of influenza on Dec 31 (day 0) was 29 and on day 5 there were 32 cases. Define variables: t = time in days since Dec 31C = number of cases a. Assume this situation is linear. Write a formula for this situation b. Use your linear formula to determine when the number of cases will hit 128. days from Dec 31 ( show work)arrow_forward8. A new car tends to depreciate in value more quickly during the first couple of years and then at a more gradual rate afterwards. Suppose that a 2017 Toyota Prius has a value of $18,000 on January 1, 2019. If it then begins to depreciate in value $1,500 per year, find a) The linear equation for the value of the car years after 2019. V b) The slope of the equation is of the car decreases c) Find the value of the car in 2022. and means for each year past 2019, the value and in 2027arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305657960
Author:Joseph Gallian
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780135163078
Author:Michael Sullivan
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:9780980232776
Author:Gilbert Strang
Publisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:9780077836344
Author:Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education