
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
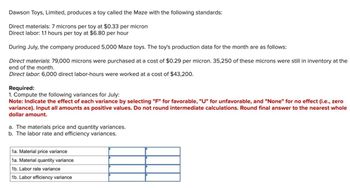
Transcribed Image Text:Dawson Toys, Limited, produces a toy called the Maze with the following standards:
Direct materials: 7 microns per toy at $0.33 per micron
Direct labor: 1.1 hours per toy at $6.80 per hour
During July, the company produced 5,000 Maze toys. The toy's production data for the month are as follows:
Direct materials: 79,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.29 per micron. 35,250 of these microns were still in inventory at the
end of the month.
Direct labor. 6,000 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $43,200.
Required:
1. Compute the following variances for July:
Note: Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero
variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the nearest whole
dollar amount.
a. The materials price and quantity variances.
b. The labor rate and efficiency variances.
1a. Material price variance
1a. Material quantity variance
1b. Labor rate variance
1b. Labor efficiency variance
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I need help understanding how to solve thisarrow_forwardA chemical engineer at Western Refining estimated the total cost for a diesel fuel desulfurization system at $2.3 million. If the direct cost factor is 1.55 and the indirect cost factor is 0.43, what is the total equipment cost? Both factors apply to delivered equipment cost.arrow_forwardA firm's production function can be written as:Q = 5LKwhere Q represents output per day. The unit costs of inputs are $150 for labor (L) and$1,000 for capital (K). Determine the least cost combination of L and K when output isproduced at the rate of 1,000 tons per day. Determine the required outlay for 1,000 tons perday.arrow_forward
- A survey of total project construction costs for a wide range of buildings (hospitals, schools, banks, nursing homes, etc.) in 2006 found that the average cost was $13,136,431. The mechanical and electrical portions of that cost were $2,511,893 and $1,585,384, respectively. If the total project cost in 2017 increases to $15,700,000, what would the mechanical portion of the total cost equal, provided the percentage (a) remained the same as in 2006, and (b) increased by 20% from the 2006 portion?arrow_forwardParadise Pottery had the following costs in May when production is 800 ceramic pots: materials, $8,700; labor (variable), $2,900; depreciation, $1,100; rent, $900; and other fixed costs, $1,500. If production changes to 900 units, how much will the total variable costs and total fixed costs be, respectively?arrow_forwardAn engineer who owns a construction company that specializes in large commercial projects noticed that material costs increased at a rate of 1% per month over the past 12 months. If a material cost index were created for that year with the value of the index set at 100 at the beginning of the year, what is the value of the index at the end of the year? Express your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forward
- Mirtha owns an online jewelry store that specializes in earrings. In March, she sells 50 pairs of earrings priced at $15. The cost of materials to create the 50 pairs of earrings was $100. The website she uses to sell her wares costs her $10 a month, and she is also charged 4% on each sale by the company that processes debit/credit card purchases. Which of the following best represents Mirth’s total cost? Group of answer choices A)The $750 Mirtha earned from earring sales minus the materials ($100), online website charge ($10), and payment processing charge (4%) B)The sum of the materials ($100), website charge ($10), and 4% payment processing charge (4%) C)The cost of all the materials used to create the earrings, $100 D)The costs of materials minus the costs it takes to run her business through the online store, in this case the $10 website charges and the 4% payment processing chargearrow_forwardClassify the following costs into either being product cost or period cost:(a) Raw material costs(b) Income taxes paid(c) Interest expenses on borrowed funds(d) Wages incurred in producing products(e) Fire insurance premium paid on factory buildings(f) Electric bill for the warehouse operation(g) Salary paid for engineers(h) Material handling cost related to production(i) Salary paid for plant managerU) Leasing expense for forklift trucks in warehouse operation(k) Mortgage payments on factory buildingsarrow_forward8 The cost of lumber per million board feet (MBF) in January 2007 was $464.49 when the value of the ENR materials cost index (MCI) was 2583.52. If the cost of lumber increased in proportion to the MCI, what was the value of the index when the cost of lumber was $400 per MBF?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education