Question
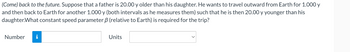
Transcribed Image Text:(Come) back to the future. Suppose that a father is 20.00 y older than his daughter. He wants to travel outward from Earth for 1.000 y
and then back to Earth for another 1.000 y (both intervals as he measures them) such that he is then 20.00 y younger than his
daughter. What constant speed parameter 3 (relative to Earth) is required for the trip?
Number i
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- : Find kinetic energy, potential energy, total energy and binding energy of an artificial satellite orbiting at a height 3600 km above the surface of the earth. [Given: Mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg, radius of the earth = 6400 km mass of satellite = 10³ kg and G = 6.67 × 10-¹1 S.I. unit.arrow_forwardAn asteroid of mass 331 kg orbits the sun in a long-period orbit of 225 years. It is currently at its furthest distance from the sun: 1.11 x 10+13 m. It is moving at 184 m/s.When the asteroid makes its closest approach to the sun in another 112 years it will pass within 1.55 x 10+10 m of the sun. How fast will it be going?arrow_forward19arrow_forward
- 10) Taking the age of Earth to be about 4 ✕ 109 years and assuming its orbital radius of 1.5 ✕ 1011 m has not changed and is circular, calculate the approximate total distance Earth has traveled since its birth (in a frame of reference stationary with respect to the Sun). _____ marrow_forwardProblem 3. A tracking station determines that an Earth-observation satellite has perigee and apogee altitudes of 350 and 1,206 km, respectively. Determine the orbital period (in minutes) and the parameter p.arrow_forward4. A satellite 300 miles above the city in a circular orbit about the Earth is directly over a particular city at time t=0. It is traveling eastward at 16,000 mph. At the same time, a small rock very near the satellite is released from rest 300 miles above the city. How does the acceleration of the rock compare to that of the satellite in both magnitude AND direction? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios