
Data Structure Using C++ (Queue) C++ code (NOT JAVA C++ JUST)
C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE PLEASE ::
We can use a queue to simulate the flow of customers through a check-out line in a store. In this simulation we will have the following details:
- one check-out line
- the expected service time for each customer is one minute (However, they may have to wait in line before being serviced)
- between zero and two customers join the line every minute
We can simulate the flow of customers through the line during a time period n minutes long using the following
Initialize the queue to empty.
for ( minute = 0 ; minute < n ; ++minute )
{
if the queue is not empty, then remove the customer at the front of the queue.
Compute a random number k between 0 and 3.
If k is 1, then add one customer to the line.
If k is 2, then add two customers to the line.
Otherwise (if k is 0 or 3), do not add any customers to the line.
}
In addition, the algorithm will keep track of the following:
- the total number of customers served
- the combined total wait time of all customers
- the maximum length of time any of these customers spent waiting in line
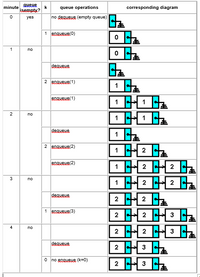
Operations on the Queue for the Check-out Line Simulation
Given a time of 5 minutes, the following demonstrates the operations on the queue:
use 1.png
this is for test the program ::
use 2.png
nd you can use these thing ::::
struct node { int data; node *next; node(int d,node *n=0) { data=d; next=n; } }; class stack { node *topp; public: stack(); void push(int el); bool pop(); int top(); bool top(int &el); //~stack(); //void operator=(stack &o); //stack(stack &o); }; stack::stack() { topp=0; } void stack::push(int el) { topp=new node(el,topp); } bool stack::pop() { if(topp==0) return false; node *t=topp; topp=topp->next; delete t; return true; } int stack::top() { if(topp!=0) return topp->data; } bool stack::top(int &el) { if(topp==0) return false; el=topp->data; return true; }
please need a full code without any errors

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Overview In this assignment, you will gain more practice with designing a program. Specifically, you will create pseudocode for a higher/lower game. This will give you practice designing a more complex program and allow you to see more of the benefits that designing before coding can offer. The higher/lower game will combine different programming constructs that you have been learning about, such as input and output, decision branching, and a loop. Higher/Lower Game DescriptionYour friend Maria has come to you and said that she has been playing the higher/lower game with her three-year-old daughter Bella. Maria tells Bella that she is thinking of a number between 1 and 10, and then Bella tries to guess the number. When Bella guesses a number, Maria tells her whether the number she is thinking of is higher or lower or if Bella guessed it. The game continues until Bella guesses the right number. As much as Maria likes playing the game with Bella, Bella is very excited to play the game…arrow_forwardPart C: Function, for and plotting We did a project in the lecture on calculating the free fall speeds and plotting them on a graph. This part is similar to the project. An engineer has derived a relationship between the force applied to a material and the extension in length that the force would cause. The relationship between force f and extension e is given by: You are asked to plot a graph showing the relationship between force and extension. You are asked to complete the following tasks: Task 1 Write a Python function which returns the value of e for a given input f. Do not use literals (e.g. 5.5, 10) in the expressions for e in the function. Instead you should define constants and use them. Note that the relationship between e and f depends on whether f is bigger than 10 or not, this means you need a certain Python construction in your function. If you can't think of that, have a look at Part A of Lab03.arrow_forwardSPIM simulator (QtSpim). Simulation: Write a MIPS program that computes the expression; y = A * B + C * D Where A, B, C, and D are integersarrow_forward
- Vocabulary Task (C language) Natural language processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence that seeks to develop the ability of a computer program to understand human language. Usually, the first step of an NLP system is to convert words into numeric codes. Thus, the system converts an input text into a sequence of numeric codes before any high-level analysis. This process is known as text preprocessing. We can only perform text preprocessing if we have a vocabulary of words and their associated numeric codes. Your task is to create a vocabulary of unique words for a given text file and assign a different number from 1 to N to each unique word, with N being the total number of unique words. You must perform this assignment so that the first word in alphabetical order gets the number 1, the second word in alphabetical order gets the number 2, and so on. A word is a sequence of letters (uppercase or lowercase). The file is composed of letters and white spaces (spaces, tabs,…arrow_forwardArtificial Intelligence (Part - 2) ==================== The Towers of Hanoi is a famous problem for studying recursion incomputer science and searching in artificial intelligence. We start with N discs of varying sizes on a peg (stacked in order according to size), and two empty pegs. We are allowed to move a disc from one peg to another, but we are never allowed to move a larger disc on top of a smaller disc. The goal is to move all the discs to the rightmost peg (see figure). To solve the problem by using search methods, we need first formulate the problem. Supposing there are K pegs and N disk. (2) What is the size of the state space?arrow_forwardusing System; class HelloWorld { static void Main() { int rows=21; int columns=76; for(int i=0;i<rows;i++) //for loop for printing the pattern for 21 rows { for(int j=1;j<=columns;j++) //for loop for printing the pattern in 76 columns { if((i+j)%7!=1 ) //if the addition of i and j does not give remainder of 1 when divided by 7 then Console.Write("-"); //print dash - on console else //otherwise peint a space on console Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(); //print a newline for printing on new row... } } }arrow_forward
- The code box below defines a variable route as a list of directions to navigate a maze. Each instruction is one of the following four basic commands: higher move one step in the positive y direction • lower. move one step in the negative y direction • left: move one step in the negative x direction • right: move one step in the positive x direction Define a function step that takes two arguments, a location (as a tuple of x and y coordinates) and an instruction (higher, lower, left, right) as a string. Given the provided location, it should return the new location (as a tuple of x and y coordinates) when following the specified instruction. If the instruction is invalid, the old location should be returned. Use the function step to determine the final position when starting from the point (0, -4) and following all instructions in the list route. Assign this final position to the variable final_point.arrow_forwardContext: Measuring Air Quality Levels of various air borne pollutants such as Nitrogen Monoxide (NO), Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) and particulate matter (also called particle pollution) are all major contributors to the measure of overall air quality. For instance, NO2 is measured using micrograms in each cubic metre of air (㎍/m3). A microgram (㎍) is one millionth of a gram. A concentration of 1 ㎍/m3 means that one cubic metre of air contains one microgram of pollutant. To protect our health, the UK Government sets two air quality objectives for NO2 in their Air Quality Strategy The hourly objective, which is the concentration of NO2 in the air, averaged over a period of one hour. The annual objective, which is the concentration of NO2 in the air, averaged over a period of a year. The following table shows the colour encoding and the levels for Objective 1 above, the mean hourly ratio, adopted in the UK. Index 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Band Low Low Low Moderate Moderate Moderate High…arrow_forwardArtificial Intelligence (Part - 1) ==================== The Towers of Hanoi is a famous problem for studying recursion in computer science and searching in artificial intelligence. We start with N discs of varying sizes on a peg (stacked in order according to size), and two empty pegs. We are allowed to move a disc from one peg to another, but we are never allowed to move a larger disc on top of a smaller disc. The goal is to move all the discs to the rightmost peg (see figure). To solve the problem by using search methods, we need first formulate the problem. Supposing there are K pegs and N disk. (1) Propose a state representation for the problem?arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





