
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
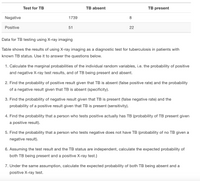
Transcribed Image Text:Test for TB
TB absent
TB present
Negative
1739
8
Positive
51
22
Data for TB testing using X-ray imaging
Table shows the results of using X-ray imaging as a diagnostic test for tuberculosis in patients with
known TB status. Use it to answer the questions below.
1. Calculate the marginal probabilities of the individual random variables, i.e. the probability of positive
and negative X-ray test results, and of TB being present and absent.
2. Find the probability of positive result given that TB is absent (false positive rate) and the probability
of a negative result given that TB is absent (specificity).
3. Find the probability of negative result given that TB is present (false negative rate) and the
probability of a positive result given that TB is present (sensitivity).
4. Find the probability that a person who tests positive actually has TB (probability of TB present given
a positive result).
5. Find the probability that a person who tests negative does not have TB (probability of no TB given a
negative result).
6. Assuming the test result and the TB status are independent, calculate the expected probability of
both TB being present and a positive X-ray test.}
7. Under the same assumption, calculate the expected probability of both TB being absent and a
positive X-ray test.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Disks of polycarbonate plastic from a supplier are an- alyzed for scratch and shock resistance. The results from 100 disks are summarized as follows: shock resistance high low scratch high 70 9 resistance low 16 5 (a) If a disk is selected at random, what is the probability that its scratch resistance is high and its shock resistance is high? (b) If a disk is selected at random, what is the probability that its scratch resistance is high or its shock resistance is high? (c) Consider the event that a disk has high scratch resistance and the event that a disk has high shock resistance. Are these two events mutually exclusive?arrow_forwardWhat are alpha levels?arrow_forwardWhat are the Class 1 error rate and the Class 0 error rate on the test data?arrow_forward
- Use ANOVA.arrow_forwardDescribe a situation where you would use a test of significance on the difference between the means of two populations by stating a pair of populations composed of the same type of individuals and a quantitative variable on those populations. You may want to mention hypotheses, the sizes of samples from those populations, and the degrees of freedom of your test statistic.arrow_forwardHello, I need help to differentiate incidence cases, and prevalence. Thanks!arrow_forward
- /transcript Call centers typically have high turnover. The director of human resources for a large bank has compiled data on about 70 former employees at one of the bank's call centers. The accompanying table shows this data. In writing an article about call center working conditions, a reporter has claimed that the average tenure is no more than two years. Formulate and test a hypothesis using these data to determine if this claim can be disputed. Use a level of significance of 0.05. Click the icon to view the call center data. Is there sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level of significance that the average tenure is no more than two years? Determine the null hypothesis, Ho, and the alternative hypothesis, H₁. Ho ... H₁: (Type whole numbers.) le Learrow_forwardThe best depiction of a population characteristic is a(an): Dependent variable Statistic Independent variable Parameterarrow_forwardWhat is a practical example that would use ANOVA?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
