
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
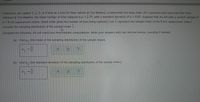
Transcribed Image Text:Customers can replace 1, 2, 3, or 4 tires at a time for their vehicle at Tire Masters, a nationwide tire shop chain. For customers who have had their tires
replaced at Tire Masters, the mean number of tires replaced is u = 2.75, with a standard deviation of o= 0.65. Suppose that we will take a random sample of
n3D8 tire replacement orders. (Each order gives the number of tires being replaced.) Let r represent the sample mean of the 8 tire replacement orders.
Consider the sampling distribution of the sample mnean x.
Complete the following. Do not round any intermediate computations. Write your answers with two decimal places, rounding if needed.
(a) Find u- (the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean).
(b) Find o- (the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample mean).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the mean and standard error of the mean of the sampling distribution. Then sketch a graph of the sampling distribution. The prices of photo printers on a website are normally distributed with a mean of $238 and a standard deviation of $67. Random samples of size 33 are drawn from this population and the mean of each sample is determined.arrow_forwardAssume that final exam scores in a given course are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 10 points. In a class of 200 students, how many would you expect to fail the exam (i.e., score less than 60) (note: scores can only be approximately normally distributed, because the minimum score is 0, but this should not alter the answer, given how large the mean is relative to the standard deviation).arrow_forwardBecause the mean is very sensitive to extreme values, it is not a resistant measure of center. By deleting some low values and high values, the trimmed mean is more resistant. To find the 10% trimmed mean for a data set, first arrange the data in order, then delete the bottom 10% of the values and delete the top 10% of the values, then calculate the mean of the remaining values. Use axial loads (pounds) of aluminum cans listed below for cans that are 0.0111 in. thick. Identify any outliers, then compare the median, mean, 10% trimmed mean, and 20% trimmed mean. 247 261 269 273 275 280 282 282 284 285 285 287 290 292 293 296 296 299 311 507 Identify any outliers. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA. The outlier(s) is/are pounds. (Type a whole number. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) C OB. There are no outliers.arrow_forward
- A standardized exam's scores are normally distributed. In a recent year, the mean test score was 1539 and the standard deviation was 315. The test scores of four students selected at random are 1940, 1290, 2240, and 1420. Find the z-scores that correspond to each value and determine whether any of the values are unusual. The z-score for 1940 is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The Z-score for 1290 is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The Z-score for 2240 is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The Z-score for 1420 is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Which values, if any, are unusual? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice. OA. The unusual value(s) is/are. CD (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) OB. None of the values are unusual.arrow_forwardA standardized exam's scores are normally distributed. In a recent year, the mean test score was 1458 and the standard deviation was 312. The test scores of four students selected at random are 1860, 1220, 2150, and 1340. Find the z-scores that correspond to each value and determine whether any of the values are unusual. The z-score for 1860 is (Round to two decimal plaes as needed.)arrow_forwardAssume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find P87, the 87-percentile. This is the temperature reading separating the bottom 87% from the top 13%.P87 = °Carrow_forward
- If we meet these conditions, the sampling distribution of the mean will have a normal shape and ... The mean of the sampling distribution will be u, (i.e., the same as the population mean) and the standard deviation of the sampling distribution will be (that's the population standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size). In the AP Stats Guy video, he talks about the number of text messages his students send during class. Suppose the average number of text messages his students send during class is u = 30 text messages. If we take samples of say, n = 36 students at a time, we would expect the mean of the sampling distribution we create to be the same as the population mean, 30 text messages. If we can further say that standard deviation of the number of text messages is 12 text messages, by how much would we expect the sample means to vary? (hint, use the formula above) text messagesarrow_forwardA standardized exam's scores are normally distributed. In a recent year, the mean test score was 1506 and the standard deviation was 317. The test scores of four students selected at random are 1940, 1230, 2190, and 1400. Find the z-scores that correspond to each value and determine whether any of the values are unusual. The z-score for 1940 is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman