
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two converging lenses are separated by 25.0 cm. The focal length of each lens is 12.0 cm. An object is placed 36.0 cm to the left of the lens that is on the left. Determine the final image distance relative to the lens on the right.
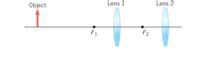
Transcribed Image Text:Object
F1
Lens 1
F2
Lens 2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a darkened room, a burning candle is placed 1.63 m from white wall. A lens is placed between candle and wall at a location that causes a larger, inverted image to form on the wall. When the lens is moved 86.6 cm toward the wall, another image of the candle is formed. K 1.63 m How far apart are the two object distances that produce these images? Answer in units of m. Find the focal length of the lens. Answer in units of m.arrow_forwardA diverging lens has a focal length of magnitude 17.8 cm. (a) For an object distance of 44.5 cm, determine the following. What are the image distance and image location with respect to the lens? (Give the magnitude of the distance in cm.) image distance cm image location in front of the lens v Is the image real or virtual? virtual What is the magnification? Is the image upright or inverted? upright (b) For an object distance of p2 = 13.4 cm, determine the following. What are the image distance and image location with respect to the lens? (Give the magnitude of the distance in cm.) image distance cm image location in front of the lens v Is the image real or virtual? ---Select--- What is the magnification? Is the image upright or inverted? upright (c) For an object distance of p3 = 26.7 cm, determine the following. What are the image distance and image location with respect to the lens? (Give the magnitude of the distance in cm.) image distance cm image location in front of the lens v Is…arrow_forwardA contact lens is made of plastic with an index of refraction of 1.54. The lens has an outer radius of curvature of +1.95 cm and an inner radius of curvature of +2.47 cm. What is the focal length of the lens? cm Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward
- Two lenses, one converging of focal length 10.0 cm and one diverging of 5.0 cm, are placed 30.0cm apart. An object is placed 20.0 cm in front of the converging lens. Determine the location and magnification of the final image with respect to the original object.arrow_forward7. A lighted candle is placed 40.0 cm in front of a diverging lens. The light passes through the diverging lens and on to a converging lens (f = 10.0 cm) that is placed 9.00 cm from the diverging lens. The final image is real, inverted, and 35.0 cm beyond the converging lens. Find the focal length of the diverging lens. cm 0 ssf6 ssf60 ssf 60 ssf607 ssf60arrow_forwardA diverging lens has a focal length of magnitude 22.2cm. Find the magnification for the object at distance 44.4 cm. Find the magnification for the object at distance 22.2 cm. Find the magnification for the object at distance 11.1 cm.arrow_forward
- When two lenses are used in combination, the first one forms an image that then serves as the object for the second lens. The magnification of the combination is the ratio of the height of the final image to the height of the object. A 1.20 cm-tall object is 60.0 cm to the left of a converging lens of focal length 40.0 cm. A second converging lens, this one having a focal length of 60.0 cm, is located 300 cm to the right of the first lens along the same optic axis. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of The eye's lens. Part A Find the location and height of the image (call it I₁) formed by the lens with a focal length of 40.0 cm. Enter your answers in centimeters separated by a comma. s₁, y = 120,2.40 cm Submit Correct Set Up: Apply Solve: Lens 1: m₁ = Previous Answers Part B $1 f₁ $1-f₁ $₂,|y₂| = 1 S s' 1 S +1/1 = = gives (60.0 cm) (40.0 cm) 60.0 cm-40.0 cm to each lens. m₁ 120 cm 60.0 cm = = -2.00 = Y'₁ Y1 120 cm and m2 $1…arrow_forwardConsider the optical system shown in the figure. The lens and mirror are separated by d = 1.00 m and have focal lengths of f₁ = +87.5 cm and f₂= = -53.4 cm, respectively. An object is placed p = 1.00 m to the left of the lens as shown. Lens LL -1.00 m Object distance location (a) What is the distance (in cm) and location of the final image formed by light that has gone through the lens twice? (Give the magnitude of the distance and select its location with respect to the lens.) ---Select--- -1.00 m- cm Mirror (b) Determine the overall magnification of the image. (c) State whether the image is upright or inverted. upright invertedarrow_forwardA lens forms an image of an object. The object is 16.0 cm from the lens. The image is 12.0 cm from the lens on the same side as the object. (a) What is the focal length of the lens? Is the lens converging or diverging? (b) If the object is 8.50 mm tall, how tall is the image? Is it erect or inverted? (c) Draw a principal-ray diagram.arrow_forward
- In the following three scenarios, an object is located on one side of a converging lens. In each case, you must determine if the lens forms an image of this object. If it does, you also must determine the following. whether the image is real or virtual whether the image is upright or inverted the image's location, q the image's magnification, M The focal length is f = 60.0 cm for this lens. Set both q and M to zero if no image exists. Note: If q appears to be infinite, the image does not exist (but nevertheless set q to 0 when entering your answers to that particular scenario). (a) The object lies at position 60.0 cm. (Enter the value for q in cm.) q= cmM= Select all that apply to part (a). realvirtualuprightinvertedno image (b) The object lies at position 7.06 cm. (Enter the value for q in cm.) q= cmM= Select all that apply to part (b). realvirtualuprightinvertedno image (c) The object lies at position 300 cm. (Enter the value for q in cm.) q= cmM= Select all that…arrow_forwardThe figure shows an object and its image formed by a thin lens. Assume that d1 = 0.781 m, d2 = 0.604 m, and h = 7.50E-2 m. What is the image height (in m; answer sign and magnitude)?arrow_forwardI need Help please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON