
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Considering the Wheatstone Bridge from Figure 3, what is the maximum value of R3 that this network is able to measure? Hint: Consider the maximum range that the potentiometer can be set to, and use the Before the Lab equations to calculate.
R3 Max =
Please answer in typing format please ASAP for
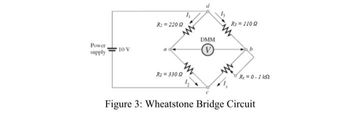
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure 3: Wheatstone Bridge Circuit**
This diagram illustrates a Wheatstone Bridge circuit, commonly used in electrical measurements to precisely measure an unknown resistance. The circuit consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape, with a power supply and a Digital Multimeter (DMM) connected across the bridge.
- **Power Supply:** A 10 V source is connected between points a and b.
- **Resistors:**
- \( R_1 = 220 \, \Omega \) connected between points a and d.
- \( R_2 = 330 \, \Omega \) connected between points a and c.
- \( R_3 = 110 \, \Omega \) connected between points d and b.
- \( R_x = 0 - 1 \, \text{k}\Omega \) (variable resistor) connected between points c and b.
- **Current Flow:**
- \( I_1 \) flows through \( R_1 \).
- \( I_2 \) flows through \( R_2 \).
- \( I_3 \) flows through \( R_3 \).
- \( I_4 \) flows through \( R_x \).
- **Digital Multimeter (DMM):** The voltmeter is used to measure the voltage between points c and d.
The objective in this setup is to adjust \( R_x \) until the DMM reads zero volts, indicating that the bridge is balanced and the ratio of the two known resistors equals the ratio of the unknown resistor to the fourth resistor. This allows the calculation of the unknown resistance precisely.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How do find the equivalent resistance of multiple resistors configures in parallel? You sum the resistances together and then divide by the number of resistors You average all of the individual resistor values. You calculate: 1/ (1/R1 + 1/R2 + + 1/Rn) ... You use the smallest resistor value.arrow_forwardSolve it with explanation.arrow_forwardHi, I was given this circuit and I have been asked to find the maximum current i that would flow in the circuit if the value Rt and Rd had very low (negligible) values. Can you help me with it?arrow_forward
- Q2/ When two resistors are connected in parallel, the total resistance is given by R = R1R2/ (R1 + R2)' what will be the worst possible error in the total resistance if the resistors are 50 Q with a 10% accuracy and 100 Q with a 5% accuracy?arrow_forwardExplain diagramarrow_forwardA Wheatstone bridge circuit is shown in Figure below, where R1=R:=R=1202, R. represents a resistance-temperature detector (RTD), and voltage source V, = 10 v. Provide the answers to questions 23 – 30. R, R, R,arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,