
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
1. Consider two sleds that are connected by a rope. The first sled has a mass of 50 kg, while the second sled has a mass of 60 kg. If a force of 200 N acting in the direction along the East is pulled by a rope connected to the first sled,
A.) determine the acceleration of the sled and
B.) the tension in the rope connecting the two sleds.
Example is attached below. Please refer to it when answering.
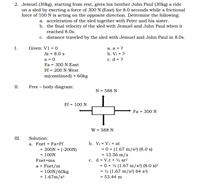
Transcribed Image Text:2. Jemuel (30kg), starting from rest, gives his brother John Paul (30kg) a ride
on a sled by exerting a force of 300 N (East) for 8.0 seconds while a frictional
force of 100 N is acting on the opposite direction. Determine the following:
a. acceleration of the sled together with Peter and his sister.
b. the final velocity of the sled with Jemuel and John Paul when it
reached 8.0s.
c. distance traveled by the sled with Jemuel and John Paul in 8.0s.
I.
Given: V1 = 0
a. a = ?
At = 8.0 s
a = 0
b. Vr = ?
c. d = ?
Fa = 300 N East
Ff = 200 N West
m(combined) = 60kg
II.
Free – body diagram:
N = 588 N
Ff = 100 N
Fa = 300 N
W = 588 N
III.
Solution:
b. Vi = V1 + at
= 0 + (1.67 m/s2) (8.0 s)
= 13.36 m/s
c. d = Vịt + ½ at²
= 0 + ½ (1.67 m/s2) (8.0 s)2
= ½ (1.67 m/s2) 64 s2)
a. Fnet = Fa+Ff
= 300N + (-200N)
= 100N
Fnet=ma
a = Fnet/m
= 100N/60kg
= 1.67m/s?
= 53.44 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Need a typed answer by keyboard Handwritten answer not allowarrow_forward1. Describe what you saw in the context of Newtons third law (equal and opposite forces): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Be careful here - where does the force of thrust come from? a. Which direction does the force of thrust point? Draw a free-body-diagram. Check that this makes sense given your answer to above.arrow_forwardConstruct free-body diagrams for the following objects; label the forces according to type. Use the approximation that g = ~10 m/s2 to determine the magnitude of all forces and the net force and acceleration of the object. 1. A 2-kg box is at rest on a table. 2. A 2-kg box is free-falling from the table to the ground.arrow_forward
- 2. In the figure below Block A has a mass of 30.0 kg and Block B has a mass of 10.0 kg. Both blocks are resting on frictionless surfaces. a) Draw the free body diagram and kinetic diagrams of each block. b) Determine the acceleration of the blocks. c) Determine the tension in the cord.arrow_forward9. The block and the bucket are connected by a string and pulley as shown. Assume that the string and pulley is massless. Mass of the block is 28.0 kg and mass of bucket is 35.0 kg. a) Draw the free body diagrams for each block b) Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks. c) Find the magnitude of the force of tension. 28.0 kg 7arrow_forwardTwo boxes are connected by a massless string across a massless frictionless pulley. Box S has a mass M and box H has a mass m as shown. a) Do a free-body diagram for these objects. b) Write Newton's Second Law equation for these objects, horizontal component only for box S and vertical component only for box H. c) Solve algebraically for the acceleration of the boxes. d) Given M=8.4 kg and m=5.7 kg, use your equation from part c) to find the value of the acceleration. e) Use this answer to find the tension in the string.arrow_forward
- A 40. kg block is placed on a ramp inclined thirty degrees to the horizontal as seen in the figure below. A horizontal force of 35 Newtons is placed on the block. If the coefficient of static friction is: 4, = 0.65 will the block remain stationary on the ramp or will it slide? 1) Sketch a free-body-diagram for this situation, include an axis. 2) Analyze the free body diagram using Newtons 2nd law. 3) Calculate f 4) Calculate fi marc 5) Draw a conclusion (circle one) F The block slides down the ramp The block remains stationary 30.0⁰ The block slides up the ramparrow_forward6. A postwoman pushed a box at rest weighing 255 N at a constant force of 22.0 N. a) Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces that may apply. b) What was the acceleration of the moving box? c) How far would it move in 3.00 seconds?arrow_forwardIf a car is moving under driving force (there is engine force), also there is air resistance and friction force acting on it, then the free body diagram of the car is: a. Motion engine mg b. Motion Fongine mgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON