
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
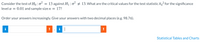
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the test of Ho :
:o?
13 against H1 : oʻ # 13. What are the critical values for the test statistic Xo2 for the significance
level α -
0.01 and sample size n
17?
Order your answers increasingly. Give your answers with two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).
i
Statistical Tables and Charts
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The manufacturer claims that your new car gets 32 mpg on the highway. You suspect that the mpg is more for your car. The 69 trips on the highway that you took averaged 35.7 mpg and the standard deviation for these 69 trips was 12.4 mpg. What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer z-test for a population proportion t-test for a population mean The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: ? p μ Select an answer ≠ = < > H1:H1: ? μ p Select an answer ≠ > = < The test statistic ? t z = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is ? > ≤ αα Based on this, we should Select an answer reject fail to reject accept the null hypothesis. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest that the population mean is not significantly more than 32 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically insignificant…arrow_forwardThe US Department of Energy reported that 48% of homes were heated by natural gas. A random sample of 331 homes in Oregon found that 132 were heated by natural gas. Test the claim that proportion of homes in Oregon that were heated by natural gas is different than what was reported. Use a 1% significance level. Give answer to at least 4 decimal places. What are the correct hypotheses? (Select the correct symbols and use decimal values not percentages.) H0: H1: Based on the hypotheses, compute the following:Test Statistic = p-value = Based on the above we choose to The correct summary would be: that the proportion of homes in Oregon that were heated by natural gas is different than what the DOE reported value of 48%.arrow_forward20arrow_forward
- Four brands of lightbulbs are being considered for use in the final assembly area of the Ford F-150 truck plant in Dearborn, Michigan. The director of purchasing asked for samples of 100 from each manufacturer. The numbers of acceptable and unacceptable bulbs from each manufacturer are shown below. At the .05 significance level, is there a difference in the quality of the bulbs? (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) H0: There is no relationship between quality and manufacturer. H1: There is a relationship. 1. Reject H0 if X2 >____ 2. X2 = ____ (Reject or Do Not Reject) H0. Ther (is a/is no) relationship between quality and manufacturer.arrow_forwardYou are testing the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is larger than the proportion of women who own cats. You sample 190 men, and 113 own cats. You sample 50 women, and 24 own cats. Find p (p-bar), as a decimal, rounded to two decimal places. Find the test statistic, rounded to two decimal places. Submit Question 9:24 PM 5/20/2021arrow_forwardFor a special pre–New Year’s Eve show, a radio station personality has invited a small panel of prominent local citizens to help demonstrate to listeners the adverse effect of alcohol on reaction time. The reaction times (in seconds) before and after consuming four drinks are in data below. At the 0.005 level, has the program host made his point? Identify and interpret the p-value for the test. Data: Subject Before After 1 0.32 0.39 2 0.39 0.44 3 0.36 0.49 4 0.41 0.53 5 0.37 0.46 6 0.42 0.52 7 0.41 0.52 8 0.43 0.46 9 0.39 0.55 10 0.41 0.52 11 0.35 0.45 12 0.42 0.41 13 0.32 0.54 14 0.39 0.46 15 0.41 0.53 16 0.33 0.54 17 0.43 0.46 18 0.42 0.43 19 0.41 0.52 20 0.35 0.52 21 0.39 0.41 22 0.39 0.44 23 0.32 0.50 24 0.33 0.53 25 0.31 0.45 26 0.35 0.45 27 0.31 0.45 28 0.32 0.48 29 0.38 0.54 30 0.37 0.46 31 0.39 0.49 32 0.30 0.51 33 0.40 0.49 34 0.41 0.50 35 0.41 0.53 36 0.35 0.47 37 0.37 0.51 38 0.41 0.46arrow_forward
- Available below are amounts of arsenic in samples of brown rice from three different regions. The amounts are in micrograms of arsenic and all samples have the same serving size. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the three samples are from populations with the same mean. Do the amounts of arsenic appear to be different in the different regions? Given that the amounts of arsenic in the samples from region C have the highest mean, can we conclude that brown rice from region C poses the greatest health problem? view the data table of the arsenic amounts. Arsenic Amounts (micrograms) A 4.9 4.9 4.9 5.2 5.3 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 6.1 6.3 B 2.3 3.6 4.5 4.6 4.8 4.8 4.8 5.1 5.1 5.4 5.4 5.5 C 5.7 5.7 6.7 6.9 7.1 7.2 7.2 7.3 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 What are the hypotheses to test? H0: mu 1 equals mu 2 equals mu 3μ1=μ2=μ3 H1: At least one…arrow_forwardYou want to compare differences in prior arrests across ethnicity in your study, you measured ethnicity as white =0 black =1 hispanic=2, and other =3. Prior arrests was recorded as the number of prior arrests. which test would you perform to see if arrests differ across diffrent ethnic categories? A. ANOVA B. T-testarrow_forwardplease help me find the test statistic and p-value!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman