
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168390
Author: Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
8a.
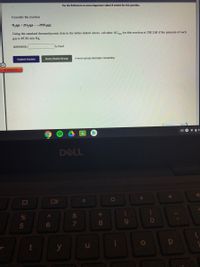
Transcribed Image Text:Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
Consider the reaction
N2(g) + 202(g) 2NO2(g)
Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AG, for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each
gas is 47.35 mm Hg.
ANSWER:
kJ/mol
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
4 more group attempts remaining
In progress
Next
US O vI 9=
DELL
&
7
8.
y
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the reaction NO(g)+NO2(g)N2O3(g) , use tabulated thermodynamic data to calculate H and S. Then use those values to answer the following questions. (a) Is this reaction spontaneous at 25°C? Explain your answer. (b) If the reaction is not spontaneous at 25°C, will it become spontaneous at higher temperatures or lower temperatures? (c) To show that your prediction is accurate, choose a temperature that corresponds to your prediction in part (b) and calculate G . (Assume that both enthalpy and entropy are independent of temperature.)arrow_forwardMethane can be produced from CO and H2.The process might be done in two steps, as shown below, with each step carried out in a separate reaction vessel within the production plant. Reaction 1 CO(g)+2H2(g)CH3OH(l) S = -532 J/K Reaction 2 CH3OH(l)CH4(g)+12O2(g) S= +162 J/K NOTE: You should be able to work this problem without using any additional tabulated data. (a) Calculate H for reaction 1. (b) Calculate Gf for CO(g). (c) Calculate S° for O2(g). (d) At what temperatures is reaction 1 spontaneous? (e) Suggest a reason why these two steps would need to be carried out separately. Substance Hf (kJ mol-1) Gf (kJ mol-1) S (J mol-1 K-1) CO(s) -110.5 197.674 CH3OH( l ) -238.7 -166.4 126.8 CH4(g) -74.8 186.2arrow_forwardThe reaction shown below is involved in the refining of iron. (The table that follows provides all of the thermodynamic data you should need for this problem.) 2Fe2O3(s)+3C(s,graphite)4Fe(s)+3CO2(g) (a) Find H for the reaction. (b) S for the reaction above is 557.98 J/K. Find S° for Fe2O3(s). (c) Calculate G for the reaction at the standard temperature of 298 K. (There are two ways that you could do this.) (d) At what temperatures would this reaction be spontaneous? Compound Hf (kJ mol-1) S° (kJ mol-1) Gf (J mol-1 K-1) Fe2O3(s) -824.2 ? -742.2 C(s, graphite) 0 5.740 0 Fe(s) 0 27.3 0 CO2(g) -393.5 213.6 -394.4.83arrow_forward
- Using tabulated thermodynamic data, calculate G for these reactions. (a) Fe(s)+2HCl(g)FeCl2(s)+H2(g) (b) 3NO2(g)+H2O(l)2HNO3(l)+NO(g) (c) 2K(s)+Cl2(g)2KCl(s) (d) Cl2(g)+2NO(g)2NOCl(g) (e) SiCl4(g)Si(s)+2Cl2(g)arrow_forwardUsing tabulated thermodynamic data, calculate G for these reactions. (a) Mg3N2(s)+6H2O(l)2NH3(g)+3Mg(OH)2(s) (b) 4CH3NH2(g)+9O2(g)4CO2(g)+10H2O(l)+2N2(g) (c) Fe3O(s)+4CO(g)3Fe(s)+4CO2(g) (d) P4O10(s)+6H2O(l)4H3PO4(aq)arrow_forward10.51 The combustion of acetylene was used in welder's torches for many years because it produces a very hot flame: C2H2(g)+52O2(g)2CO2(g)+H2O(g) H= -1255.5 kJ (a) Use data in Appendix E to calculate S for this reaction, (b) Calculate G and show that the reaction is spontaneous at 25°C. (c) Ls there any temperature range in which this reaction is not spontaneous? (d) Do you think you could use Equation 10.4 to calculate such a temperature range reliably? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- On the basis of your experience, predict which of the following reactions are spontaneous. (a) CO2(s)CO2(g) at 25°C (b) NaCl(s)NaCl(l) at 25°C (c) 2NaCl(s)2Na(s)+Cl2(g) (d) CO2(g)C(s)+O2(g)arrow_forwardAt 298 K, G = 70.52 kJ for the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) (a) Calculate _G at the same temperature when PNO = 1.0 104 atm, PO2=2.0103 atm, and PNO2=0.30 atm. (b) Under the conditions in part a, in which direction is the reaction spontaneous?arrow_forwardWhen ammonium chloride is added to water and stirred, it dissolves spontaneously and the resulting solution feels cold. Without doing any calculations, deduce the signs of G, H, and S for this process, and justify your choices.arrow_forward
- For the reaction C2H2(g)+4F2(g)2CF4(g)+H2(g) S is equal to 358 J/K. Use this value and data from Appendix 4 to calculate the value of S for CF4(g).arrow_forwardGiven that H f for HF(aq) is -320.1 kJ/mol and S for HF(aq) is 88.7 J/mol K, find Ka for HF at 25C.arrow_forwardCalculate G forH2O(g)+12O2(g)H2O2(g) at 600. K, using the following data: H2(g)+O2(g)H2O2(g)K=2.3106at600.K2H2(g)+O2(g)2H2O(g)K=1.81037at600.Karrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning