
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
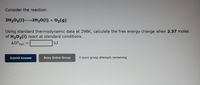
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the reaction:
2H202(1) 2H20(1) + 02(g)
Using standard thermodynamic data at 298K, calculate the free energy change when 2.37 moles
of H202(1) react at standard conditions.
AG°rxn
kJ
Retry Entire Group
9 more group attempts remaining
Submit Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction: 2H₂S(g) + 30₂(g) 2H₂O(g) + 2SO₂(g) Using standard thermodynamic data at 298K, calculate the free energy change when 2.13 moles of H₂S(g) react at standard conditions. AG rxn kj Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardFor the reaction 2H₂O(1)→ 2H₂(g) + O2(g) AG 461 kJ and AH = 572 kJ at 339 K and 1 atm. This reaction is B favored under standard conditions at 339 K. The entropy change for the reaction of 1.81 moles of H₂O(1) at this temperature would be Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 2 more group attempts remaining J/K.arrow_forwardEntropy Example: If AS°¸ =-198.3 J/K, is the reaction spontaneous at 25°C sys N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 • AS univ = AS sys + AS surr > ? • AS surr =-(AHsys)/T Determine the AHrxn • AH˚4 N2(g) = 0 kJ/mol f • AH°+ H2(g) = 0 kJ/mol f • AH° NH 3(g) = -46.19 kJ/mol farrow_forward
- Entropy Example: If AS°¸ =-198.3 J/K, is the reaction spontaneous at 25°C sys N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 • AS univ = AS sys + AS surr > ? • AS surr =-(AHsys)/T Determine the AHrxn • AH˚4 N2(g) = 0 kJ/mol f • AH°+ H2(g) = 0 kJ/mol f • AH° NH 3(g) = -46.19 kJ/mol farrow_forwardConsider the reaction: I2(g) + Cl2(g) 2ICI(g) Using standard thermodynamic data at 298K, calculate the free energy change when 2.030 moles of I2(g) react at standard conditions. AG°rxn = kJ Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardPlease step by step answer and current answer pleasearrow_forward
- The reaction 2 C4H10(g) + 13O2(g) - has AG° = -5407 kJ. Determine the value of AG°, for C4H10(8). 8 CO2lg) + 10 H20(g) Standard Free Energies of Formation of Typical Substances at 298.15 K TABLE 18.2 Substance Substance Substance AG? (kJ mol ') AG? (kJ mol-") AG? (kJ mol ) Agt) CaO6) -604.2 K,SO,G) -1316.4 AgC6) -109.7 Ca(OH),() -896.76 N,() Al() 0.00 CaSO) NH,(g) NH.CI() -1320.3 -16.7 ALĻO,6) C) (graphite) COO Co,( -1576.4 CaSO, H,OG) -1435.2 - 203.9 CaSO,2H,0G) -1795.7 NO(g) + 86.69 NO,(g) N,O) N,0, -137.3 +51.84 -394.4 Fe() +103.6 CH( -50.79 Fe,O,6) -741.0 +98.28 CH,A(g) -58.6 Na() CH,OH() -166.2 H,0(g) -228.6 Na,CO,() -1048 CO(NH)l) -197.2 -237.2 NaHCO,6) -851.9 CO(NH)(ag) C,H,(g -203.8 HCI -95.27 NaC) -384.0 +209 HNO,) -79.91 NaOH) -382 +68.12 H,SO() -689.9 Na,SO.) -1266.8 HC,H,0,(/) Hg(/) Hg(g) -32.9 -392.5 C,H,OH() -174.8 PbO) -189.3 +17.3 +31.8 Ca(o) K() SO;(g) -300.4 Ca00,() -1128.8 KCI) -408.3 -370.4 CaC,6) -750.2 i kJ e Textbook and Media Choose the value of K, for the…arrow_forwardConsider the reaction H,(g) + F2(g) 2HF(g) Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of HF(g) is reduced to 20.42 mm Hg, while the pressures of H,(g) and F,(g) remain at 1 atm. ANSWER: kJ/mol Submit Answer Retry Entire Group No more group attempts remain Previous Next Save and Exit Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support OPEN FILES MacBook Air EZ F8 F9 F10 F1 FIarrow_forwardCalculate the AS°rxn of the following reaction at 223°C and standard pressure. 1st attempt O See Hint C,H,(8) + 30,(g) . 200,(g) + 2H,0(g) AH°f, kJ/mol S°, J/mol K AG°F, kJ/mol C2H4(g) 52.3 219.5 68.1 O2(g) 205.0 CO2(g) -393.5 213.6 -394.4 H20(g) -241.8 188.7 -228.6 J/mol Karrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardab Lock Fn 50 Esc Why is the exothermic reaction below spontaneous at all temperatures? Select the correct answer below: O Because AH is positive and AS is positive. Because AH is negative and AS is positive. O Because AH is negative and AS is negative. O Because AH is positive and AS is negative. 1 ! F1 A N F2 8 2 W S X Alt F3 3 E D F4 C $ TiCl4 (9) + 2H₂O(g) → TiO2 (s) + 4HCI(g) पं F5 R F % 5 V F6 T G < 6 F7 B DELL H F8 7 N F9 *00 M F10 5 2 F11 Alt 3 F12 P PrtScr "R Ctrl { [ ? Ins Pa Uarrow_forwardThermodynamics For Practice 18.6 Enhanced - with Feedback Part A Consider the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 : SO2(g)+,O2(g)→SO3(9) Calculate AGxn at 25° C. IXI Express your answer with the appropriate units. ΔΗ (kJ/mol) Reactant or S° product (J/mol · K) SO2 -296.8 248.2 O2 205.2 SO3 -395.7 256.8 AGn Value Units You may want to reference (Pages 820 - 826) Section 18.8 while completing this problem.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY