
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the pulley system depicted in the figure. The block is prevented from moving by the applied force F. Assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless.
T₂ =
T3 =
T₁ =
T5 =
(a) Determine the tension in each section of rope. (Use the following as necessary: M and g.)
T₁ =
Ⓡ
F =
T₁ T₂
T₁
F =
T5₂
M
T3
(b) Find the magnitude of F. (Use the following as necessary: M and g.)
(c) What If? What should the magnitude of the force F be if the mass M is to have an upward acceleration of magnitude a? (Use the following as necessary: M, g, and a.)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given:-
We have given that the system of pully and mass M is as shown in the figure as
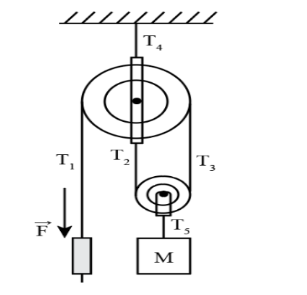
Find:-
a) The Tension as shown in the figure
b) The magnitude of the force
c) What If? What should the magnitude of the force be F if the mass M is to have an upward acceleration of magnitude a?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Needs Complete solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardCompute the resultant of the concurrent forces shown in N. P1 = 265 N, P2= 303 N, P3 = 455 N, P4 = 192 N, 01 = 21, 02= 25, and 03= 10. Write numerical value only in 2 decimal places. P1 P4 03 8₂ + Y 0₁ P3 P2 + Xarrow_forwardWhat is T?arrow_forward
- A 1,480-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force of 350 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. F 20.0° / 20.0° a b (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) (b) If the 350-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a). m/s²arrow_forwardIn the figure, three masses are attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block B lies on a frictionless table. mA = 5.4 kg, mB = 6.2 kg, and mc = 10.7 kg. Find the tension in the cord to the right (between masses B and C) once the blocks have been released and are free to move. Your answer should be in N: Question Help: Read Barrow_forwardThree objects are connected as shown in the figure. The strings and frictionless pulleys have negligible masses. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25 and static friction is 0.30. Block A has a mass of 3 kg and block B has a mass of 4 kg. a) What is the maximum mass block C can have before block B will start to move? b) If block C has a mass of 7 kg. and was 1 m above the ground, how long would it take block C to hit the ground starting from rest?arrow_forward
- A heavy sled is being pulled by two people, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between the sled and the ground is H = 0.603, and the kinetic friction coefficient is µ = 0.403. The combined mass of the sled and its load is m = 336 kg. The ropes are separated by an angle o = 25.0°, and they make an angle 0 = 31.1° with the horizontal. Assuming both ropes pull equally hard, what is the minimum rope tension required to get the sled moving? minimum rope tension: If this rope tension is maintained after the sled starts moving, what is the sled's acceleration? m/s2 acceleration:arrow_forwardPROBLEM SET 06: Interacting Objects, Tension, Pulleys OPEN a T₁= B Find the magnitude of the tension in each of the three cables supporting the traffic light if it weights w=335 N and a = 20°, 8=83. You may click the image to enlarge. Help on how to format answers: units. T₁= T- Turned in automatically when due Instructions Aarrow_forwardTwo muscles in the back of the leg pull upward on the Achilles tendon, as shown in the figure. (These muscles are called the medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle.) Find the magnitude, in newtons, of the total force on the Achilles tendon.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON