
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Consider the panels A-D in Figure 1. Which one panel illustrates the segregation of alleles on chromosomes in a cell of genotype M/m; B/b undergoing anaphase I of meiosis?
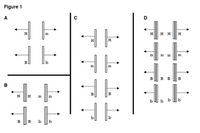
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 1
A
D
HE
M
m
M
м
M
M
M
im
m
B
·J.. ·
m
B
В
В
B
B
B
M
M
m
m
b
В
B
b
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I am not sure how to explain what parent the nondisjunction occurred from in example 2 part 1. Sometimes nondisjunction will occur in a parent that has normal chromosome numbers and result in an offspring that has abnormal number of chromosomes. The phenotype of the affected offspring will often allow geneticists to determine in which parent and during which division of meiosis the nondisjunction occurred. In each of the examples below, assume the parents have a normal diploid chromosome complement. EXAMPLE 1: A man with the X-linked dominant condition “brown tooth enamel” and a woman with normal tooth enamel produce a son with brown tooth enamel. Let’s call the allele for brown tooth enamel “XB” and normal tooth enamel “Xb”. In which parent did the nondisjunction occur? Explain and/or illustrate Did nondisjunction occur at meiosis I or II? Explain and/or illustrate. What sex chromosomes are in the child’s somatic cells? EXAMPLE 2: The parents in the family above produce another…arrow_forwardThe following image shows Nondisjunction. Which of the following cells will suffer from a genetic disorder due to the occurence of Nondisjunction: Nondisjunction A DOO m+1 n+1 n-1 Number of (a) Nondisjunction of homologous chromosomes in melosis I n-1 n n+1 More than 1 of the answers Meiosis II Nondisjunction Gametes A 000 n.1 mosomes (b) Nondisjunction of si chromatics in meloearrow_forwardif a species of animal has 18 chromosomes in its diploid cells (2n=18). Describe what the metaphase chromosome arrangement would look like for this species in each of the following stages: mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis Ilarrow_forward
- Draw a haploid mitosis of the genotype a+ ; b.arrow_forwardA cell goes through meiosis in order to separate a set of replicated chromosomes into two haploid cells and then to separate these cells again without copying the DNA to form four haploid cells. The following diagram illustrates how chromosomes are divided up during the two splits in meiosis. For each split in meiosis, you will see three different representations of chromosome division. Select the answer option for each split that correctly shows the way meiosis divides the chromosomes. Which one shows the Second Meiosis Split?arrow_forwardUSING TWO DIFFERENT COLORS TO SIGNIFY THE MATERNAL AND PATERNAL CHROMOSOMES, DRAW THE RESPECTIVE CELLS IN EACH LABELED PHASE OF MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS. THE CHROMOSOME NUMBER WILL BE "4" AND SHOULD BE REPRESENTED AS TWO HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS. MAKE SURE YOU USE TWO DIFFERENT SIZES FOR EACH OF THE PAIRS. BELOW EACH PHASE, BRIEFLY DESCRIBE WHAT HAPPENS. MITOSIS ΜEIOSIS I MEIOSIS II Crossing over needs to be illustrated ACCURATE CELL NUMBER IS NEEDED МЕТАРНАSE ΑΝΑΡHASE МЕТАРНASEI ANAPHASE I МЕТАРНАSE II ANAPHASE IIarrow_forward
- Page 1 of 1 USING TWO DIFFERENT COLORS TO SIGNIFY THE MATERNAL AND PATERNAL CHROMOSOMES, DRAW THE RESPECTIVE CELLS IN EACH LABELED PHASE OF MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS. THE CHROMOSOME NUMBER WILL BE "4" AND SHOULD BE REPRESENTED AS TWO HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS. MAKE SURE YOU USE TWO DIFFERENT SIZES FOR EACH OF THE PAIRS. BELOW EACH PHASE, BRIEFLY DESCRIBE WHAT HAPPENS. MITOSIS MEIOSIS I Crossing over needs to be illustrated in one of the homologous pairs and carried through the remaining drawings METAPHASE ANAPHASE METAPHASE I MEIOSIS II Accurate number of cells are needed ANAPHASE I METAPHASE II ANAPHASE IIarrow_forwardDiagram A represents a chromosomal inversion event. A, B, C, D, E, F, are chromosomal loci. Represents a centromere. Diagram B shows a crossing over event between non-sister chromatids of a non-inverted and an inverted chromosome (darker vs. lighter lines) during meiosis I. Which of the following represents a recombinant chromosome resulting from the cross-over event shown in diagram B? А А в с D E MARK ALL THE ANSWES THAT APPLY. Inversion E B F B B EEEE B F F E в F A E D D с в А F В в F A E D в Аarrow_forwardIn 1965 a faulty study was performed, which suggested that the XYY karyotype was associated with violent antisocial criminal behavior. The study was later disproven, as there is no association between an additional Y chromosome and abnormal behavior. Explain how this karyotype could arise in someone by mentioning the sex of the affected person, the identity of the parent (mother or father) in which the non-disjunction occurred, and the specific meiotic division during which non-disjunction took place.arrow_forward
- Part of the karyotype of a diploid individual who is heterozygous for one chromosomal rearrangement is shown in the diagram. The chromosomes involved in the rearrangement, and their homologous pair, are shown. The location of each gene is labeled using horizontal lines and the name of each gene is labeled using letters or numbers. Answer the following questions about the diagram. A. What rearrangement is shown? Be as specific as possible. B. Describe a mutation scenario that could cause this rearrangement to be formed. A B D E F G H IXI A B с D E IIXDD 1 2 3 4 5 6 F G H D 1 2 34 5 6 Xarrow_forwardAs two students, who will be designated Student J and Student K, were studying together, they argued about the differences between Mitosis and Meiosis (both Meiosis I and Meiosis II). Student J maintained that it if they were looking at very good slides under the microscope and concentrated on Metaphase, it would be possible to tell the difference between the cells undergoing Mitosis, the cells undergoing Meiosis I, and the cells undergoing Meiosis II. Student K said it would be impossible to tell which nuclear division was occurring. Assume there are three unlabeled sets of very good slides of the cells of the common pea plant with one set showing Mitosis, one set showing Meiosis I, and one set showing Meiosis II. To repeat, the slides are unlabeled so the students don’t know which process is occurring in which set. However, the students know that the common pea plant has 14 total chromosomes (or 7 pairs of chromosomes). Explain carefully what Student J would be looking for at the…arrow_forwardThe genes F and G are on the same chromosome in a eukaryote. Using a microscope, you can see that a chiasma occurs between these two loci in 24% of the meioses. A double heterozygote could have genotype FG//fg, where the // represents the pair of homologous chromosomes that contain the F and G loci: one homolog contains F and G alleles and the other contains f and g. You cross this FG//fg individual to an fg//fg individual and examine their offspring. What proportion of the offspring do you expect to be Fg//fg? Group of answer choices 48% 6% None of these 12% 24%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education