
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
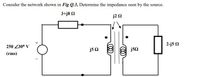
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the network shown in Fig Q.3, Determine the impedance seen by the source.
3+j8 2
j2 2
2-j5 2
250 230° V
j5 Q
j50
(rms)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help me please IN THE CIRCUIT SHOWN, THE VALUE OF THE CURRENT SOURCE IS IN RMS VALUE. DETERMINE: A) THE VOLTAGE (ONLY THE MAGNITUDE) AT THE INDUCTOR TERMINALS, VL B) THE VOLTAGE (ONLY THE MAGNITUDE) AT THE RESISTOR TERMINALS, VR C) THE AVERAGE POWER ABSORBED BY THE 40 Ω RESISTORarrow_forwardDetermine the equivalent impedance of the network shown in Figure if the frequency is f= 60 Hz. Then compute the current i(t) if the voltage source is v(t) = 50 cos (wt+30°) V. Finally, calculate the equivalent impedance if the frequency is f= .400 Hz i(t) R = 25 v(t) L=20 mH C=50 μFarrow_forwardAnswer subparts D,E,Farrow_forward
- Unless given, use the: POLAR FORM for voltage and current, RECTANGULAR OF 5 FORM for impedance. Consider the following circuit, supplied by a 10VRMS current source with a 0° phase shift (i.e. Vsource = 1020° V). R1 C (2 V sine 50 Hz 100 Q 16 μF L 320 mH a. What is the total impedance of the circuit? b. Is the circuit inductive, capacitive, or neither (resistive)? c. What is the total power (apparent) delivered by the current source? d. Draw the phasor diagram of the voltage and current at the source. e. What is the current passing through the R2 and L branch? f. Draw the phasor diagram of the voltage and current at the R2 and L branch. ww R2 100arrow_forwardA circuit consists of a series connected 84 Ω resistor and a 163 mH inductor. The circuit supply is a 121 V rms source with a frequency of 42 Hz. Ultimately, you need to calculate the average power dissipated in the circuit. You should have found the polar form of the complex current. The average power dissipated in the resistive and reactive circuit is: ?=??cosφ where φ is the phase of the current, and V and I are the rms values. Finally, calculate the circuit Power Factor (cos?) where φ is the phase of the current. Finally, will the circuit Power Factor cos? be lagging or leading?arrow_forwardSubject: Network Theory Please solve this qarrow_forward
- A three phase 390 volt (line voltage) distribution system feeds power to a household load. Each phase of the system (distribution line) has an impedance consisting of a resistance (0.602) and a reactance (0.40) (inductive). The system is connected to three-phase load with an impedance of j +62 in a delta connection. What is the active, reactive and apparent power of the load (notice that distribution line impedance is not part of the load)? Give the answers to two decimal places. a) Absolute value of current feeded by the voltage source. I = 3.62 A Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 3.62 b) Active power P = c) Reactive power Q = d) Apparent power S (absolute value) kVA = kW kV Ar 4arrow_forwardA 110V(rms), 60HZ AC source is connected to a motor, which can be represented by a resistor and an inductor connected in series. There is also a 56µF capacitor connected across the motor (parallel to the source). Source is providing 1KVA at 73% lagging power factor. Draw a well-labeled circuit diagram and determine: (1) Magnitude of the source Current (ii) Active and reactive power of the motor (iii) Power factor of the motor (iv) Magnitude of the motor current (v) Motor resistor and inductor valuearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,