
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Consider the
1. Which of the following is undergoing General Planar Motion?
2. Which of the following is closest to the velocity at point B?
3. Which of the following best approximates the velocity at point C?
4. Which of the following approximates the location of Instantaneous Center of Rod BC?
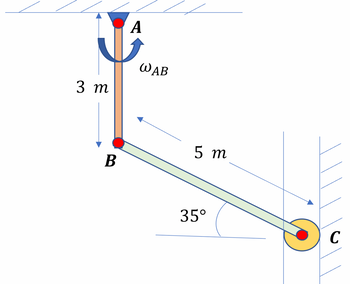
Transcribed Image Text:3 m
B
A
WАВ
5 m
35°
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hand written please.arrow_forward(b) The disk cam is controlled by the 5" slotted arm AB through a pin P fixed on the disk. If at the instant shown, 0 = 60°, 0 = -0.1 rad/s, and 6 = -0.2 rad/s², find the angular velocity w and the angular acceleration a of the disk at the instant. O is at the 9 o'clock position P is at the 6 o'clock position. II 발 20 O C F5 F6 B 3" A F7 R=4" 8 F8 F9 prt sc F10 home F11 end F12arrow_forward4. In the mechanism shown in the figure, rocking rod OA rotates about axis O with a uniform angular velocity a, OA=r, 00=1. At this moment, OAL00; , determine the angular velocity and angular acceleration of rocker O,B.arrow_forward
- The combined pulley shown has two cables wound around it at different diameters and fastened to point A and block E, respectively. Member ABOCD rotates counter clockwise to lift block E. If the total acceleration of point D is 5 in/s²Z45° at the instant shown, determine: a) the angular velocity of member ABCD3; b) the angular acceleration of member ABCD; c) the velocity of block E. Ø5" F Ø3" 5" B C, E 4" 8" 4"arrow_forwardRod AB is attached to the rotating arm using ball-and-socket joints as shown in (Figure 1). AC is rotating with a constant angular velocity of WAC = 8.5 rad/s about the pin at C. Assume d = 5 ft. Figure 2 ft 1.5 ft 3 ft B do @AC 1 of 1 Part Determine the components of the angular velocity of link BD at the instant shown. Enter your answers in radians per second to three significant figures separated by commas. (WDB)x, (WDB)y, (WDB)z = Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer VE ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec ? rad/s Next >arrow_forwardThe system shown in the figure is composed of bar AB which is pin-supported at A and attached to bar BC. The end of bar BC is connected to the slider block C. At the instant shown, the acceleration of point B is 1.125 m/s2 downward and the angular velocity of bar BC is 0.5625 rad/s counterclockwise. What is the angular acceleration of bar BC?arrow_forward
- The flywheel shown has an angular velocity of 600 rpm. The connecting rod AB slides through the pivoting collar at C. When 0= 45°, find @AB, the angular velocity of AB. Hint: The direction of the velocity of the bar AB at a point directly under C is parallel to the collar C. That direction can be found from trigonometry. A 16" Barrow_forwardAnother very common basic mechanism is the "four-bar" (the ground is considered one of the bars). The class has designed this demonstration four-bar with dimensions 2.2ft , 4.6ft and 1.0ft . In the position shown, coupler BC is horizontal, rocker CD is vertical and are easily found), and crank AB is rotating at a constant angular (therefore dimensions velocity of 11.8 rad/s Determine the angular velocity of rocker CD. NOTE: Magnitude should be entered here, direction in part 2 of this problem. A LAB WAB B 0A counterclockwise. LAD LBC D LCDarrow_forwardThe double gear shown in Figure: Q 6(b) rolls on the stationary lower rack; the velocity of its center A is 1.4 m/s directed to the right and an acceleration of 3.2 m/s² to the right. If the lower rack is stationary, determine (i) the angular acceleration of the gear and (ii) the acceleration of points B, C, and D of the gear. B R VA=1.4 m/s D aa=3.2 m/s² = 160 mm ľ2= 110 mm Figure: Q 6(b)arrow_forward
- At the instant shown in (Figure 1), rod AB has an angular velocity WAB = 2.2 rad/s and an angular acceleration AB = 10 rad/s². The collar at C is pin-connected to CD and slides over AB. Part A Determine the angular velocity of rod CD at this instant. Express your answer in radians per second to three significant figures. Enter positive value if the direction of velocity is counterclockwise and negative value if the direction of velocity is clockwise. Figure 60° WAB αAB 0.75 m Do 0.5 m 1 of 1 ΜΕ ΑΣΦ. Η vec WCD= Submit Request Answer Part B ? rad/s Determine the angular acceleration of rod CD at this instant. Express your answer in radians per second squared to three significant figures. Enter positive value if the direction of acceleration is counterclockwise and negative value if the direction of acceleration is clockwise. αCD= Η ΜΕ ΑΣΦ VAΣ IT vec Submit Request Answer B < Return to Assignment Provide Feedback ? rad/s²arrow_forward(Three-Dimensional Motion) The figure below represents a pair of bevel gears A and B. Gear A rotates in ahorizontal plane about a vertical axis at O. Gear B rotates around the shaft OC which in turn rotates about the terminal axis at O. determine the angular accelera tion of gear B when gear A is stationary and member OC has an angular velocity of 10j rad/sec and and angular acceleration of 25j rad/sec2 .arrow_forwardfirst 3 partsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY