
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
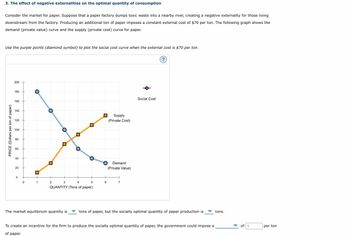
Transcribed Image Text:3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantity of consumption
Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living
downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $70 per ton. The following graph shows the
demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper.
Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $70 per ton.
PRICE (Dollars per ton of paper)
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
0
1
4
5
QUANTITY (Tons of paper)
2
3
The market equilibrium quantity is
Supply
(Private Cost)
O Demand
6
(Private Value)
7
Social Cost
?
tons of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is
To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government could impose a
of paper.
tons.
of $
per ton
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate private market equilibrium and the socially optimal equilibrium for the following negative production externality. (note: demand and supply functions are already in the inverse format) Demand: P = 100 - Q Supply: P=-50 + 2Q Marginal External Cost: MEC = 2Q Private Market Equilibrium = Socially Optimal Equilibrium = (enter your responses rounded to a whole number)arrow_forwardI chose option D and got this wrong. I thought that when you had a positive externality The demand curve move to the right. Wouldn’t this mean that the level of output and the price would be greater than the free market ones? can you explain how my answer is wrong? What is correct?arrow_forwardThis is an end-of-chapter problem that I'm struggling with! thanks!arrow_forward
- In the market for widgets, consumers have a market demand (marginal benefit) curve of P = MB = 250 - Q. In this problem, there is no distinction between private and social marginal benefit. The widget suppliers have a market supply (private marginal cost) curve of P = MC Private = 100+ Q. The production of widgets generates a negative externality in the form of pollution, with marginal external cost of X = 50. Due to this externality, there will be a difference between private and social marginal cost. Questions Analyze the following scenarios describing possible outcomes in the market for widgets. Efficient Outcome Find the equation for social marginal cost (MCsocial), using the information above. Determine the efficient quantity (Q*). AGEC 3503 1 ● HW7 - Negative Externalities Calculate the joint surplus (JS*), total external cost (TX*), and the total surplus (TS*) based on the efficient quantity. Equilibrium Outcome Find the market equilibrium, defined by the market quantity (Q) and…arrow_forwardAir pollution creates a negative externality—a cost suffered by a third party as a result of an economic transaction. A standard solution to a negative externality is a Pigouvian tax, a tax that raises the marginal private cost of pollution emissions to the level of the marginal social cost. The socially optimal quantity of pollution emissions is then determined by the intersection of the marginal private benefit, or demand, curve and the marginal social cost curve. The article notes that "putting a dollar value on the benefits of cleaner air has been difficult." Assuming this problem has been resolved, in the accompanying diagram, move the endpoints of line Smarginal social cost to show the marginal social cost curve. Then move the line labeled "Tax" to show the amount of the tax needed to limit emissions to the socially optimal level.arrow_forwardParks confer many external benefits on society: open space, trees that reduce pollution, and so on. Therefore, the market equilibrium quantity of parks is not equal to the socially optimal quantity. The following graph shows the demand for parks (their private value), the supply of parks (the private cost of producing them), and the social value of parks, including both the private value and external benefits. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the market equilibrium quantity. Next, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to indicate the socially optimal quantity.arrow_forward
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that every alcoholic drink consumed generates roughly $2 in external economic costs. Briefly describe how you would model this externality in a supply and demand diagram (e.g. would you draw a social marginal cost curve or a social marginal benefit curve?).arrow_forwardConsider a manufactured good whose production process generates pollution. The demand for the product is Q=100-3P. The market supply function is Q=P. The marginal external cost is MEC=2Q. What is the emissions tax that needs to be imposed to achieve the social optimum? Illustrate on graph What is the economic incidence of this emissions tax? In other words, what proportion of this tax will be paid by producers of this product and what proportion of the tax will be paid by consumers?arrow_forwardThe marginal cost of educating a college student is $2,000 a year. The table shows the marginal benefit schedule of a college education. The marginal external benefit of a college education is a constant $1,000 per student per year. There are no public colleges. If the government subsidizes colleges and sets the subsidy so that the efficient number of students enroll, what is the subsidy per student, how many students enroll, and what is the cost to taxpayers? The subsidy is $ per student and million students enroll. Students (millions per year) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 Marginal benefit (dollars per student per year) 5,000 3,000 2,000 1,500 1,200 1,000 800 500arrow_forward
- In the market for a certain pesticide, the following equations represent the private demand and supply: Private Demand: QD = 160 - P Private Supply: QS = 4P The use of this pesticide has a negative externality that affects nearby ecosystems, which is not reflected in the market price. The external cost is estimated to be $5 per unit of pesticide. By how much is the pesticide overconsumed under perfect competition? A) 1 units B) 3 units C) 4 units D) 5 units E) none of the abovearrow_forwardAir horns impose many external costs on society: the risk of being deafened, the annoyance of being awakened in the middle of the night, and so on. Therefore, the market equilibrium quantity of air horns is not equal to the socially optimal quantity. The following graph shows the demand for air horns (their private value), the supply of air horns (the private cost of producing them), and the social cost of air horns, including both the private cost and external costs. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the market equilibrium quantity. Next, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to indicate the socially optimal quantity.arrow_forwardThe marginal private cost of fertilizer production is MPC = 40 + Q, where Q is the amount of fertilizer produced. The marginal benefit (both private and social) of fertilizer is MB = 340 – 4Q. In addition to the private costs faced by producers of fertilizer, people who walk or drive past the area where the fertilizer is produced also face costs because of the horrible smell of the fertilizer; the marginal external cost generated by the fertilizer is MEC = 20 + 3Q. How much fertilizer will be produced by the free market? What is the efficient quantity of fertilizer? Calculate the amount of deadweight loss in this market, and explain what this number means. Suppose that the government realizes that the current amount of fertilizer produced by the free market is inefficient and decides to correct this inefficiency by taxing the production of fertilizer. How large should the tax per unit of fertilizer be to induce the market to produce the efficient amount, and why would such a tax…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education