
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
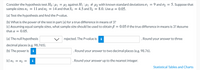
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the hypothesis test Ho :µ1 = µ2 against H1 : µ1 # µ2 with known standard deviations o1 = 9 and o2 = 5. Suppose that
sample sizes n1 = 11 and n2 = 14 and thatI = 4.5 and I2 = 8.0. Use a = 0.05.
(a) Test the hypothesis and find the P-value.
(b) What is the power of the test in part (a) for a true difference in means of 3?
(c) Assuming equal sample sizes, what sample size should be used to obtain B = 0.05 if the true difference in means is 3? Assume
that a = 0.05.
(a) The null hypothesis
rejected. The P-value is i
Round your answer to three
decimal places (e.g. 98.765).
(b) The power is
i
. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).
(c) n1 = n2 =
i
. Round your answer up to the nearest integer.
Statistical Tables and Charts
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A simple random sample of size n = 40 is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 108.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 19.6. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the α = 0.01 level of significance? Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: μ = 100 H₁: μ> 100 Compute the test statistic. to = 2.78 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. The P-value is 0.004. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the result of the hypothesis test? the null hypothesis because the P-value is the level of significance. At the α = 0.01 level of significance, the population mean less than 100. different from 100. greater than 100. less than 108.6. different from 108.6. greater than 108.6.arrow_forwardCalculate the test-statistic, t with the following information for a Two Independent Samples t Test with Ha:μ1-μ2≠0. Be sure to first determine if you need to pool or not.n1=60, ¯x1=2.53, s1=0.53n2=50, ¯x2=2.69, s2=0.96Round to 3 decimal places. t =__________ It is pool or not?________arrow_forwardA sample is randomly selected from a population with a mean of μ = 50, and a treatment is administered to the individuals in the sample. After treatment, the sample is found to have a mean of M = 56 with a standard deviation of s = 8. Which test is most appropriate to determine if there is a difference between the means? z-score test single-sample t-test independent samples t-test related-samples t-testarrow_forward
- To compare the dry braking distances from 30 to 0 miles per hour for two makes of automobiles, a safety engineer conducts braking tests for 35 models of Make A and 35 models of Make B. The mean braking distance for Make A is 43 feet. Assume the population standard deviation is 4.6 feet. The mean braking distance for Make B is 46 feet. Assume the population standard deviation is 4.5 feet. At α=0.10, can the engineer support the claim that the mean braking distances are different for the two makes of automobiles? Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed. The critical value(s) is/are Find the standardized test statistic z for μ1−μ2.arrow_forwardIf the researcher decides to test this hypothesis at the = 0.05 level of significance, determine the critical value. The critical value are=_ and=_. Round to three decimal places as needed.arrow_forwardWe collected a sample of twenty-five observations. We assumed that the observations are from a population whose values follow a normal distribution with a mean of u and a standard deviation of five. We performed a test with these hypotheses Ho: μ = 0H₁ = 0 and H₁ : μ0H₁0. The test statistic is the sample mean . The 5% rejection region is 1.959964 > 1.959964. What is the power of this test when μ = -2μ = -2? Please state the statistical power up to the fourth decimal place.arrow_forward
- Suppose the mean IQ score of people in a certain country is 100. Suppose the director of a college obtains a simple random sample of 39 students from that country and finds the mean IQ is 104.5 with a standard deviation of 13.6. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. (a) Consider the hypotheses Ho: µ= 100 versus H,: µ> 100. Explain what the director is testing. Perform the test at the a = 0.10 level of significance. Write a conclusion for the test. Explain what the director is testing. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The director is testing if the sample provided sufficient evidence that the population mean IQ score is actually not equal to 100. OB. The director is testing if the sample provided sufficient evidence that the population mean IQ score is actually greater than 100. O C. The director is testing if the sample provided sufficient evidence that the population mean IQ score is actually not greater than 100. O D. The director is testing if the sample provided sufficient…arrow_forwardScores on an IQ test are normally distributed. A sample of 25 IQ scores had variance of 64. The developer of the test claims that the population standard deviation is 15. Do these data provide sufficient evidence to significance? Use α=0.05α=0.05 . Answer the following questions. (a) What is the parameter? . (input as "mean", "standard deviation", "variance" or "proportion") (b) Determine if the alternative hypothesis is "right", "left" or "two-tailed" test. (input as "right", "left" or "two-tailed") (c) Test by using a confidence interval. Round confidence interval to nearest thousandth. (e.g. 0.1345 would be entered as 0.135) between ( and ) (d) State conclusion.: There is (input as "sufficient" or "insufficient") to (input as "conclude" or "reject") to conclude that the population standard deviation of IQ test is 15.arrow_forwardYou wish to test Ho: μ₁ μ2 versus Ha:μ₁ μ₂ at a = = 0.10. You obtain a sample of size n₁ 1 = 58.2 and a standard deviation of $₁ = 20.9 from the first population. You obtain a sample 40.2 and a standard deviation of $2 = 5.6 from the second 9 with a mean of 2 a mean of of size n2 population. = = What is the test statistic? = = 6 with Assume that the data come from normal populations with equal variances. Round your answers to three decimal places, and round any interim calculations to four decimal places.arrow_forward
- A researcher wishes to see if there is a difference between the mean number of hours per week that a family with no children participates in recreational activities and a family with children participates in recreational activities. She selects two random samples and the data are shown. Use μ1 for the mean number of families with no children. At α=0.10, is there a difference between the means? Use the P-value method and tables. (a) State the hypothesis and identify the claim with the correct hypothesis. H0: ▼(Choose one) H1: ▼(Choose one) This hypothesis test is a ▼(Choose one) test. (b)Find the critical value(s). Round the answer to 3decimal places, if necessary. If there ismore than one critical value, Critical values: (c)Compute the test value. Round the answer to at least 3 decimal places, if necessary. z= Compute the P -value. Round the answer to four decimal places. P-value= (d)Make the decision. What's the null hypothesis? (e)Summarize the…arrow_forward= You wish to test Ho: d 0 versus Ha: Md > 0 at a significance level of 0.10. For the context of this problem, d = μ2 μ₁ where the first data set represents a pre-test and the second data set represents a post-test. You obtain pre-test and post-test samples for nd 18 subjects. The average difference -= (post-pre) is d 3.8 with a standard deviation of the differences of sa 32.6. Round your answers to three decimal places, and round any interim calculations to four decimal places. What is the test statistic? - - -arrow_forwardConsider a paint-drying situation in which drying time for a test specimen is normally distributed with o = 6. The hypotheses H,: µ = 74 and H: µ < 74 are to be tested using a random sample of n = 25 observations. (a) How many standard deviations (of X) below the null value is x = 72.3? (Round your answer to two decimal places.) 1.42 standard deviations (b) If x = 72.3, what is the conclusion using a = 0.004? Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) z = p-value = State the conclusion in the problem context. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean drying time is less than 74. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean drying time is less than 74. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean drying time is less than 74. O Reject the null…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman