
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
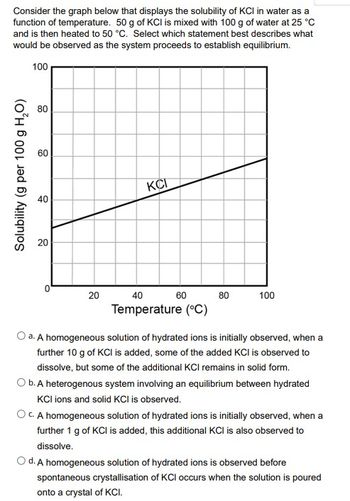
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the graph below that displays the solubility of KCI in water as a
function of temperature. 50 g of KCI is mixed with 100 g of water at 25 °C
and is then heated to 50 °C. Select which statement best describes what
would be observed as the system proceeds to establish equilibrium.
100
Solubility (g per 100 g H₂O)
80
60
40
20
0
20
KCI
40
60
Temperature (°C)
80
100
O a. A homogeneous solution of hydrated ions is initially observed, when a
further 10 g of KCI is added, some of the added KCI is observed to
dissolve, but some of the additional KCI remains in solid form.
O b. A heterogenous system involving an equilibrium between hydrated
KCI ions and solid KCI is observed.
O c. A homogeneous solution of hydrated ions is initially observed, when a
further 1 g of KCI is added, this additional KCI is also observed to
dissolve.
O d. A homogeneous solution of hydrated ions is observed before
spontaneous crystallisation of KCl occurs when the solution is poured
onto a crystal of KCI.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 0.20 mol of N2 and 2.0 mol of NO. The following reaction becomes possible: N2(g) + O2(g) = 2NO(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.693 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of N2. Round your answer to two decimal places. Шмarrow_forwardConsider the following equilibria: 2SO3(g) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) Kc1 = 2.3 × 10 – 7 2NO3(g) ⟷ 2NO2(g) + O2(g) Kc2 = 1.4 ×10 – 3 Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction: SO2(g) + NO3(g) ⟷ SO3(g) + NO2(g) A 1.3 × 10 – 2 B 1.6 × 10 – 4 C 78 D 6.1 × 103arrow_forwardSuppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 0.10 mol of CO, 0.30 mol of H,O and 1.8 mol of H,. The following reaction becomes possible: co(g) + H,0(g) =CO,{g)+H2(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.296 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H,0. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forward
- At 25 °C and 765 Torr, carbon dioxide has a solubility of 0.0342 M in water. What is its solubility at 25 °C and 1410 Tor? M S =arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.5 mol of Cl2 and 0.60 mol of HCI. The following reaction becomes possible: H2(g)+ Cl2(g) 2HCl (g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 3.73 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H2. Round your answer to two decimal places. Омarrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium reaction: PBr5(g) + 1/2 O2(g) = POB13(g) + Br2(g) Kc = 5.6 x 102 at 512 K Calculate K. for the reaction 2 PBr5(g) + O2(g) = 2 POBR3(g) + 2 Br2(g) at the same temperature. 24 1.1 x 103 280 5.6 x 102 O None of these 3.2 x 105arrow_forward
- produces N20 and oxygen. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K. for the reaction 2 N,O4(g) –2 N,0(g) + 3 O2(g) from the following information: N2(g) + ¿O2(g) =N‚O(g) K¸ = 2.7 × 10-18 N,O4(g) =2 NO;(g) K. = 4.6 × 10-3 N2(g) + 2 O2(g) =2 NO2(g) K. = 1.7× 10-17arrow_forwardDuring an experiment, O.257 mol of H2 and 0.257 mol of I2 were placed into a 1.28 liter vessel where the reaction H2(g) + 12(g) 2 2HI(g) came to equilibrium. For this reaction, Kc = 49.5 at the temperature of the experiment. What were the equilibrium concentrations of H2, 12, and HI? [H2] = M %3D [12] = M [HI] = i Marrow_forwardI need to find the mols of CO, H2O, CO2, and H2 respectively within the mixture when it reaches equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Suppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.20 mol of N2 and 1.6 mol of NO. The following reaction becomes possil N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.205 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO. Round your answer to two decimal places. Шм ✗arrow_forwardSuppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 0.80 mol of I, and 1.7 mol of HI. The following reaction becomes possible: H₂(g) +1₂(g) → 2HI(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.600 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of I2. Round your answer to two decimal places. M Xarrow_forwardGiven: 2N2(g)+ O2(g) = 2N20(g); Ke(1) = 5.8 x 10-36 and N2(g) + O2(g) = 2NO(g); K(2) = 4.1 x 10-31 What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? 2N20(g) + O2(g) = 4NO(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY