
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
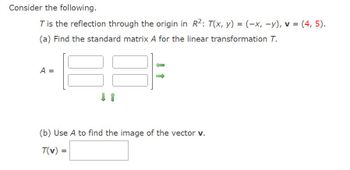
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following.
T is the reflection through the origin in R²: T(x, y) = (-x, -y), v = (4, 5).
(a) Find the standard matrix A for the linear transformation T.
A =
(b) Use A to find the image of the vector v.
T(v)
=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Assume that T is a linear transformation. Find the standard matrix of T. T: R2→R*, T(e,) = (8, 1, 8, 1), and T(e2) = (-6, 9, 0, 0), where e, = (1,0) and e, = (0,1).arrow_forward10. Let T be the linear transformation from R3 to R$ that rotates every vector around the y-axis by radians, counterclockwise as viewed from the point (0,5, 0), and afterwards multiplies its length by 4. (a) Find the matrix of transformation T. (b) Calculate T((1, 2, 3)).arrow_forwardI need help with this please help mearrow_forward
- Consider the following. T is the clockwise rotation (0 is negative) of 60° in R2, v = (1, 2). (a) Find the standard matrix A for the linear transformation T. A = (b) Use A to find the image of the vector v. T(v) =arrow_forwardDetermine the matrix of the linear transformation T(x, y) = (3x + 5y, 3y – 2x) 5 -2 3 (a) -2 3 (b) (c) 3 3 3 (d) 3 3 -2 a 2]arrow_forwardLet T : R³ → R³ be the linear transformation that does the following things, in this order, to an input vector x = [x y z]¹: (i) Interchanges the second and third coordinates of . (ii) Multiplies the first coordinate of the resulting vector by 2. (iii) Replaces the second coordinate of the resulting vector with a 0. (iv) Multiplies the resulting vector by the following matrix: 0 0 0 0 You don't have to show that T is linear. (a) The description of T given above is purely algebraic, in that it explicitly describes how to take 7 = [x y z] and write down T() in coordinates. Give a geometric description of what each of the four "steps" of applying T actually does to a vector. (Your Week 9 tutorials may help in describing what the last step does.) (b) Find the standard matrix AT of T. (c) Find a spanning set for null(AT), and describe what null(AT) is geometrically (i.e., describe it geomet- rically as a subset of R³) (d) Find a spanning set for im(AT), and describe what im(AȚ) is…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

