Question
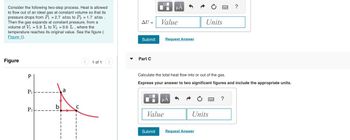
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following two-step process. Heat is allowed
to flow out of an ideal gas at constant volume so that its
pressure drops from P₁ = 2.7 atm to P2 = 1.7 atm.
Then the gas expands at constant pressure, from a
volume of V₁ = 5.9 L to V₂ = 9.6 L, where the
temperature reaches its original value. See the figure (
Figure 1).
Figure
P
P₁
P2
σ
P
D
HÅ
AU =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
1 of 1
wwwww
?
Calculate the total heat flow into or out of the gas.
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
☐
με
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images
