
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
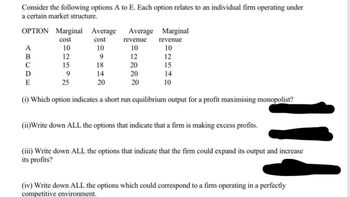
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following options A to E. Each option relates to an individual firm operating under
a certain market structure.
OPTION Marginal Average Average
cost
10
9
18
14
20
A
B
C
D
E
cost
10
12
15
9
25
revenue
10
12
20
20
20
Marginal
revenue
10
12
15
14
10
(1) Which option indicates a short run equilibrium output for a profit maximising monopolist?
(ii)Write down ALL the options that indicate that a firm is making excess profits.
114
(iii) Write down ALL the options that indicate that the firm could expand its output and increase
its profits?
(iv) Write down ALL the options which could correspond to a firm operating in a perfectly
competitive environment.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PLEASE ANSWER QUESTION C) ONLY The SolarFarm powerplant has both fixed and variable costs. As the plant expands production, it first has constant returns to scale, and then diminishing returns to scale. (a) Draw a large graph showing (only) the firm’s marginal costs and average total costs in a suitably labelled graph. Show on the graph where the firm’s technology changes from constant-returns to diminishing-returns.SolarFarm is a monopolist with a downward sloping demand curve. Add to your graph a demand and marginal revenue curve. Assume that the demand curve intercepts the average cost curve at its minimum point. Show the quantity and price of electricity in this market.(b) The government connects SolarFarm to a nearby town that is currently without electricity. Show in a new, large, graph how the market price and quantity of electricity sold change as a result.(c) Return to the situation in part (a) of this question. The government discovers a new technology that would allow…arrow_forwardAt which point is allocative efficiency attained?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a way to deter entry? OA. increase costs through legislation that affects only new entrants OB. obtain a patent so that others must license your invention OC. raise switching costs for customers that use your products OD. All of the above.arrow_forward
- Please answer with explanations or procedures of the steps following questions i) ii) iii)arrow_forward21) In Figure 5.5, what profit would the monopolist earn? P P4 P3 P2 P₁ MR Q* MC AVC D Figure 5.5 A) zero profit, because it would shut down. B) a positive profit. C) a loss less than its total fixed cost. D) a loss greater than its total fixed cost. ECON 2003: 1 ATCarrow_forwardpart D E F Garrow_forward
- Exhibit 10-4 $/0 MC ATC 24 /t 10 The non-discriminating monopolist in Exhibit 10-4 should: O Produce 10 units at a price of $36 per unit. O Produce 10 units at a price of $24 per unit. O Produce 10 units at a price of $40 per unit. O Produce 15 units at a price of $32 per unit. O We cannot determine what the firm should do without knowing its average variable cost.arrow_forwardQuestion 4 $19 16 13 10 0 100 MC 160180 210 Quantity MR ATC D Assume all monopolistically competitive firms in an industry have demand and costs similar to the firm shown. What should we expect? O Firms will exit the business and the demand curve will shift to the left This firm will produce where MR-MC and no other firms will enter or exit Other firms will enter the industry and the demand curve will shift to the leftarrow_forwardW ECON 2100 Compatibility Mode Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Share O Comments 2. Line D represents the market demand curve for polo shirts; if the polo shirt market is perfectly competitive and MC represents the market supply curve. But if the shirts are produced by a single monopoly firm, MR represents the marginal revenue curve for a monopolist producer of polo shirts and MC represents the marginal cost curve for that monopolist. 48 44 40 36 32 MC 28 20 16 12 8 4 MR 4 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 Quantity of Polo shirts a. If the polo shirts are supplied by a perfectly competitive industry, what will be the output and price? (Please explain your answer.) b. If the polo shirts are supplied by a monopoly, what will be the output and price that the monopoly would choose? (Please explain your answer.) c. Please show on the graph the dead weight loss associated with monopoly price/quantity outcome? Page 2 of 4 639 words English (United States) Focus +…arrow_forward
- 3. An industry is subject to agglomeration economies (and diseconomies). The profit per firm is £100 for an isolated firm, and increases to a maximum of £160 per firm in a cluster with 6 firms. The profit curve is linear, with a slope of +£12 in the positively-sloped part and -£10 in the negatively-sloped part. Illustrate this profit curve. What will be the equilibrium number of firms in the cluster and how much profit will each firm make? Will this be greater than the efficient number of firms? Explain why. How will an increase in transport costs affect the profit curve and the optimal cluster size? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forward12 15 UO 18 1 The reason that the "fast-casual" restaurant market is monopolistically competitive rather than perfectly competitive is because entry into the market is blocked. products are differentiated. there are many firms in the market. barriers to entry are very low. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardÑ6arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education