
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
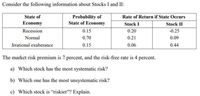
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following information about Stocks I and II:
Probability of
State of Economy
State of
Rate of Return if State Occurs
Economy
Stock I
Stock II
Recession
0.15
0.20
-0.25
Normal
0.70
0.21
0.09
Irrational exuberance
0.15
0.06
0.44
The market risk premium is 7 percent, and the risk-free rate is 4 percent.
a) Which stock has the most systematic risk?
b) Which one has the most unsystematic risk?
c) Which stock is "riskier"? Explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that many stocks are traded in the market and that it is possible to borrow at the risk-free rate, r. The characteristics of two of the stocks are as follows: Stock A B Correlation-1 Rate of return. Expected. Return 79 10% Standard Deviation 30% 70% Required: a. Calculate the expected rate of return on this risk-free portfolio? (Hint: Can a particular stock portfolio be formed to create a "synthetic" risk-free asset?) (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) b. Could the equilibrium ry be greater than rate of return? Yes Noarrow_forwardProblem 1 You are given the following information about stock X and the market portfolio, M: Riskless Asset (f) Stock X Market Portfolio (M) E(r) 0.04 (4%) ? 0.10 σ 0.00 0.30 0.20 You are not given the expected return of stock X. The correlation of the returns on the stock X and the market portfolio is equal to 0.4. a) What is the beta (6) of stock X? b) Assuming the CAPM holds, what is the expected return on stock X? c) You have $1,000 to invest in some combination of the risk-free asset, stock X, and the market portfolio. You are thinking of investing $300 in the risk free asset, $400 in stock X, and $300 in the market portfolio. What is the overall expected return, standard deviation and beta of this portfolio?arrow_forwardSuppose that stocks are exposed to systematic risks only so that stock i has the following return structure: Ri,t = mį + Si,t where mi is the average return, and si,t is the systematic risk. When we construct a portfolio including more and more stocks, which of the following would happen? The portfolio volatility gradually decreases and eventually converges to a certain positive value. ● The portfolio volatility gradually decreases and eventually converges to zero. The portfolio volatility stays unchanged.arrow_forward
- If markets are in equilibrium, which of the following conditions will exist? a. Each stock's expected return should equal its required return as seen by the marginal investor. b. All stocks should have the same expected return as seen by the marginal investor. c. The expected and required returns on stocks and bonds should be equal. d. All stocks should have the same realized return during the coming year. e. Each stock's expected return should equal its realized return as seen by the marginal investor.arrow_forwardSuppose that there are many stocks in the security market and that the characteristics of stocks A and B are given as follows: Stock expected return standard deviation A 14% 6% B 18 10 CORRELATION = -1 Suppose that it is possible to borrow at the risk-free rate, rf. What must be the value of the risk-free rate? (Hint: Think about constructing a risk-free portfolio from stocks A and B.) (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 3 decimal places.)arrow_forwardAs the number of stocks in a portfolio decrease, the portfolio's unsystematic risk will O A. increase O B. O C. D. increase 1 decrease / decrease / increasing decreasing increasing decreasing at a/an rate.arrow_forward
- 2) see picturearrow_forwardSuppose that there are many stocks in the security market and that the characteristics of stocks A and B are given as follows: Stock A B Expected Return 10% Standard Deviation 5% 9 18 Correlation = -1 Risk-free rate Suppose that it is possible to borrow at the risk-free rate, rf. What must be the value of the risk-free rate? (Hint: Think about constructing a risk-free portfolio from stocks A and B.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 3 decimal places. %arrow_forwardSuppose your expectations regarding the stock price are as follows: State of the Market Boom Normal growth Recession Probability Ending Price 0.26 $ 140 0.25 110 0.49 80 Use the equations E (r) = Ep (s) r(s) and o² = Ep (s) [r(s) — E(r)]² to compute the mean and standard deviation of the HPR on - S S Mean Standard deviation HPR (including dividends) 55.0% 21.0 -16.0 stocks. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. % %arrow_forward
- You are analyzing a stock that has the following returns given the various states of economy. State of Economy Probability Return Recession 0.12 -7.20 Normal 0.68 6.80 Boom 0.2 15.40 What is the expected return on this stock?arrow_forwardWe know the following expected returns for stocks A and B, given the different states of the economy: State(s) Probability E(rA,s) E(rB,s) Recession 0.1-0.06 0.04 Normal 0.5 0.09 0.07 Expansion 0.4 0.17 0.11 What is the standard deviation of returns for stock B?arrow_forwardConsider the following information on Stocks I and II: Probability of State of Economy State of Economy Rate of Return if State Occurs Stock I Stock II Recession .22 .045 -.37 Normal .62 .355 .29 Irrational .16 exuberance .215 .47 The market risk premium is 11.7 percent, and the risk-free rate is 4.7 percent. a. Calculate the beta and standard deviation of Stock I. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter the standard deviation as a percent and round both answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. Calculate the beta and standard deviation of Stock II. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter the standard deviation as a percent and round both answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. Which stock has the most systematic risk? d. Which one has the most unsystematic risk? e. Which stock is "riskier"? a. Beta Standard deviation b. Beta Standard deviation c. Most systematic risk d. Most unsystematic risk e. "Riskier" stock 1.94 % %arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education