
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
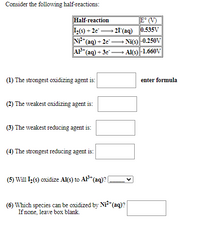
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following half-reactions:
Half-reaction
I(s) + 2e"
NP*(aq) + 2e" -
AP*(aq) + 3e -
E° (V)
- 21 (aq) 0.535V
Ni(s) |-0.250V
- Al(s) |-1.660V
(1) The strongest oxidizing agent is:
enter formula
(2) The weakest oxidizing agent is:
(3) The weakest reducing agent is:
(4) The strongest reducing agent is:
(5) Will L(s) oxidize Al(s) to AF* (aq)? (
(6) Which species can be oxidized by Ni*(aq)?
If none, leave box blank.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s) 0.799V Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s) -0.250V Zn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) -0.763V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Zn2+(aq) oxidize Ag(s) to Ag+(aq)? (yes/no) (6) Which species can be reduced by Ni(s)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) I2(s) + 2e- 2I-(aq) 0.535V Sn2+(aq) + 2e- Sn(s) -0.140V Mn2+(aq) + 2e- Mn(s) -1.180V (1) The weakest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The strongest reducing agent is: (3) The strongest oxidizing agent is: (4) The weakest reducing agent is: (5) Will I-(aq) reduce Mn2+(aq) to Mn(s)? (6) Which species can be reduced by Sn(s)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) Br2(l) + 2e- 2Br-(aq) 1.080V Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s) -0.250V Al3+(aq) + 3e- Al(s) -1.660V (1) The weakest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The strongest reducing agent is: (3) The strongest oxidizing agent is: (4) The weakest reducing agent is: (5) Will Al(s) reduce Br2(l) to Br-(aq)? (yes/no) (6) Which species can be reduced by Ni(s)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forward
- 7>) True or Falsearrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) Hg2+(aq) + 2e- Hg(l) 0.855V Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) -0.126V Mn2+(aq) + 2e- Mn(s) -1.180V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Mn2+(aq) oxidize Hg(l) to Hg2+(aq)? (yes / no) (6) Which species can be reduced by Pb(s)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) Br2(l) + 2e- 2Br-(aq) 1.080V Sn2+(aq) + 2e- Sn(s) -0.140V Al3+(aq) + 3e- Al(s) -1.660V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Br2(l) oxidize Al(s) to Al3+(aq)? (yes/no) (6) Which species can be reduced by Sn(s)?arrow_forward
- Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Consider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) C2(g) + 2e" - 2CI (aq) 1.360V 2H"(aq) + 2e H2(g) 0.000V - Mn"(aq) + 2e¯ - Mn(s)|-1.180V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Cl,(g) oxidize Mn(s) to Mn*(aq)? 2+ (6) Which species can be reduced by H,(g)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) F2(g) + 2e- 2F-(aq) 2.870V Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) -0.126V Mn2+(aq) + 2e- Mn(s) -1.180V (1) The weakest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The strongest reducing agent is: (3) The strongest oxidizing agent is: (4) The weakest reducing agent is: (5) Will F-(aq) reduce Mn2+(aq) to Mn(s)? (6) Which species can be reduced by Pb(s)? If none, leave box blank.arrow_forwardReferences Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Consider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E (V) Hq (aq) + 2e Hq(1) 0.855V 2H' (aq) + 2e H>(a) 0.000v Zn2 (aq) + 2e Zn(s) 0.763V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Wil Zn2(aq) oxidize Hgili to Hg(aq)?) (6) Which species can be oxidized by H(aq)? If none, leave box blank Submit Answer Aarrow_forward
- Consider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) Br2(l) + 2e- 2Br-(aq) 1.080V Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) -0.126V Fe2+(aq) + 2e- Fe(s) -0.440V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Fe2+(aq) oxidize Br-(aq) to Br2(l)? (yes/no) (6) Which species can be oxidized by Pb2+(aq)?arrow_forwardIncluding the state of reaction (aq),(l),(g),etc Thank youarrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Half-reaction E° (V) Br2(l) + 2e- 2Br-(aq) 1.080V Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) -0.126V Fe2+(aq) + 2e- Fe(s) -0.440V (1) The strongest oxidizing agent is: enter formula (2) The weakest oxidizing agent is: (3) The weakest reducing agent is: (4) The strongest reducing agent is: (5) Will Fe2+(aq) oxidize Br-(aq) to Br2(l)? (yes/no) (6) Which species can be oxidized by Pb2+(aq)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY