
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Consider the following galvanic cell:
|
|
E° (V) |
|
U3+ + 3 e− → U(s) |
−1.642 |
|
In3+ + 2e− → In+ |
−0.444 |
What is the potential of the galvanic cell when In3+ is 0.023 M, In+ is 0.37 M, and U3+ is 0.076 M?
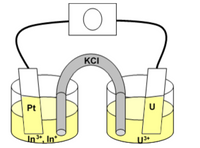
Transcribed Image Text:KCI
Pt
U
In*, In*
3+
U3+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardUse the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C. (do not assume that this is written as a spontaneous reaction, it may be written as an electrolytic cell). 3Hg2+(aq) + 2 Fe(s) → 6 Hg(1) + 2 Fe3+(aq) Hg22+ (aq) + 2e → 2 Hg(1) -> Fe3+(aq) +3 e → Fe(s) E° = +0.80 V E° = -0.04 V 1.52 V -0.76 V -0.84 V 0.84 Varrow_forwardAn electrochemical cell is based on these two half-reactions: Oxidation: Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq, 0.010 M) + 2 e− Reduction: MnO4 −(aq, 2.0 M) + 4 H+(aq, 1.0 M) + 3 e− → MnO2(s) + 2 H2O(l) Calculate the cell potential.arrow_forward
- For the cell: Zn(s) + 2H† (aq) →→ Zn2+(aq) + H2 (g) If [Zn2+] = 1 M, PH2 = 1 atm, and E = 0.123 V what is pH?arrow_forwardConsider a galvanic electrochemical cell constructed using Cr/Cr³⁺ and Zn/Zn²⁺ at 25 °C. The following half-reactions are provided for each metal: Cr³⁺(aq) + 3 e⁻ → Cr(s) E°red = -0.744 V Zn²⁺(aq) + 2 e⁻ → Zn(s) E°red = -0.763 V Given that the standard cell potential is 0.019 V and the overall equation is 2 Cr³⁺ (aq) + 3 Zn (s) → 2 Cr (s) + 3 Zn²⁺ (aq), what is the cell potential for this cell at 25 °C when [Zn²⁺] = 0.0323 M and [Cr³⁺] = 0.1736 M?arrow_forwardThe anode compartment of a galvanic cell consists of a Zn anode immersed in 0.05M ZnCl2 The cathode compartment consists of a Cu cathode immersed in an 0.10M CuCl2 solution. Using the cell potentials found on page 815 of your textbook, calculate the cell potential for this reaction. Assume T = 298K.arrow_forward
- You make a voltaic cell with copper and aluminum. If the cell potential is measured to be +2.50 V at room temperature, then what is the reaction quotient?arrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential of a cell composed of a cathode consisting of a Co wire immersed in a 1.44 M Co²+ solution and an anode consisting of a Co wire immersed in a 5.60×10-5 M Co²+ solution. Assume the temperature of the solutions is 298 K. Cell potential: Varrow_forwardConsider the following galvanic cell: E° (V) U3+ + 3 e− → U(s) −1.642 In3+ + 2e− → In+ −0.444 What is the cathode? U/U3+ In3+/In+ Pt/In3+ Pt/In+arrow_forward
- + The Nernst Equation The Nernst equation is one of the most important equations in electrochemistry. To calculate the cell potential at non-standard-state conditions, the equation i E=E 2.303 RT log10 Q where E is the potential in volts, Eo is the standard potential in volts, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature in kelvins, 12 is the number of moles of electrons transferred, Fis the Faraday constant, and is the reaction quotient. Using the common reference temperature, 25 °C or 298 K, the equation has the form E = ED (0.0592) log Q The reaction quotient has the usual form Q [products [reactants A table of standard reduction potentials gives the voltage at standard conditions, 1.00 M for all solutions and 1.00 atm for all gases. The Nernst equation allows for the calculation of the cell potential E at other conditions of concentration and pressure. Part A For the reaction 2Co²+ (aq) + 2Cl(aq) +2Co²+ (aq) + Ch₂(g). E 0.483 V what is the cell potential at 25°C if the…arrow_forward4)A galvanic cell is constructed that uses the following half-cell reactions: Cu+(aq) + e−→ Cu(s) I2(s) + 2e−→ 2I−(aq) a)Determine the cell potential for the spontaneous reaction under standard conditions. b)If the cell in part a is operated at 298 K with [Cu+] = 2.5 M and [I−] = 3.5 M, calculate the cell potential. Is the reaction spontaneous under these conditions? Explain. c)If [Cu+] was equal to 1.4 M, at what concentration of I− would the cell have zero potential?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY