
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Consider the following data from a repeated-measures design. You want to use a repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H0: µD = 0 (the null hypothesis states that the
| Observation | A | B |
| 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 3 | 5 | 7 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 8 | 9 |
What is the MD? (one decimal)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The null and alternative hypothesis is,
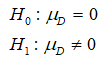
The formula for calculating the value of MD is,
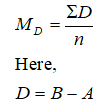
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the regression equation, letting overhead width be the predictor (x) variable. Find the best predicted weight of a seal if the overhead width measured from a photograph is 2 cm. Can the prediction be correct? What is wrong with predicting the weight in this case? Use a significance level of 0.05.arrow_forwardAssume that you want to test the claim that the paired sample data come from a population for which the mean difference is μd = 0. Compute the value of the t test statistic. x 6 5 12 3 7 y 3 74 8 4 12arrow_forwardHow do you deal with question 3 I need detailed explanationarrow_forward
- The following data represent the results from an independent-measures study comparing two treatment conditions. Treatment I II 10 7 N = 16 8 4 G = 120 7 9 ∑X² = 1036 9 3 13 7 7 6 6 10 12 2 M = 9.000 M = 6.000 T = 72 T = 48 SS = 44 SS = 56 Use an independent-measures t test with α = .05 to determine whether there is a significant mean difference between the two treatments. (Use three decimal places; subtract MIIII from MII.) t-critical = ± t = t Distribution Degrees of Freedom = 21 -3.0-2.0-1.00.01.02.03.0t Conclusion: Fail to reject the null hypothesis; there are significant differences between the two treatments. Reject the null hypothesis; there are significant differences between the two treatments. Fail to reject the null hypothesis; there are no significant differences between the two treatments. Reject the null hypothesis; there are…arrow_forwardYou are conducting a test of homogeneity for the claim that two different populations have the same proportions of the following two characteristics. Here is the sample data. Population Population Category #1 #2 A 40 102 28 84 The expected observations for this table would be Population Population Category #1 #2 A 38.02 103.98 29.98 82.02 The resulting Pearson residuals are: Population Population Category #1 #2 0.103 0.038 0.131 0.048 Chp -> Ce & 5 7. 00 16 %24 4arrow_forwardConsider the following data from a repeated-measures design. You want to use a repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H0: µD = 0 (the null hypothesis states that the mean difference for the general population is zero). The data consist of five observations, each with two measurements, A and B, taken before and after a treatment. Assume the population of the differences in these measurements are normally distributed. Observation A B 1 1 3 2 3 4 3 5 7 4 4 4 5 8 9 What is the t statistic for the repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H0: µD = 0? (two decimals)arrow_forward
- You wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.10. Ho:μ=72.2 Ha:μ≠72.2You believe the population is normally distributed, but you do not know the standard deviation. You obtain the following sample of data: Column A Column B Column C Column D Column E 102.6 66.5 52 59.2 91.1 100.3 47.4 77.7 70.8 94.7 83.9 107.6 87.7 65.4 82.3 88.2 87.7 68 60 95.3 78.4 72.9 101.4 58.3 59.2 100.3 71.6 76.1 74.9 74.9 56.2 88.2 77.7 72.9 90.6 81.1 55 86.4 78 53.6 57.3 86 94 50 85.1 105.6 92.2 70.3 73.7 59.2 81.9 78 86.4 75.7 86 What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) α greater than αarrow_forwardIn a test of hypothesis, the null hypothesis is that the population mean is greater than or equal to 37 and the alternative hypothesis is that the population mean is less than 37. The population has a normal distribution with variance of 10.6. The test is to be made at the 5% significance level. In order that the value of power at M₁ = 35. 27 to be 0.9, how large a sample do we need? O d. 20 O e. 38 O c. 6 O a. 31 O b. 63arrow_forwardTo determine if their 1.33 centimeter galvanized pipes are properly adjusted, Fogarty Manufacturing has decided to use an X-Chart which uses the range to estimate the variability in the sample. Answer Table Step 4 of 7: Use the following sample data, taken from the next time period, to determine if the process is "In Control" or "Out of Control". Observations: 1.4, 1.42, 1.38, 1.37, 1.4 Sample Mean: 1.394 Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Control Chart Copy Table Average Values The average of the selected cell(s) is 1.340. Copy Value obs1 obs2 obs3 obs4 obs5 Sample Mean Sample Range 1.34 1.29 1.35 1.33 1.35 1.3320 1.35 1.35 1.29 1.38 1.28 1.3300 1.34 1.35 1.32 1.33 1.34 1.3360 1.36 1.29 1.37 1.35 1.30 1.3340 1.29 1.31 1.33 1.32 1.38 1.3260 1.31 1.32 1.31 1.31 1.3180 1.34 1.33 1.3300 1.38 1.31 1.29 1.34 1.35 1.33 1.30 1.35 1.32 1.3300 1.34 1.37. 1.28 1.36 1.3440 1.37 1.30 1.3080 1.37 1.29 1.30 1.28 1.35 1.36 1.32 1.31 1.32 1.29 1.36 1.38 1.3400 1.3280 1.30 1.35 1.32 1.32 1.29…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman