Question
Consider the following 5 plots of concentration ?? versus position ?? across a barrier (indicated by the orange highlighting). All 5 plots are on the same scale. Assuming that the barriers all have the same area ?? and same diffusion coefficient ??, rank the (magnitude of the) rate at which molecules cross the barriers, from largest to smallest.
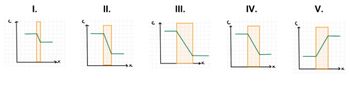
Transcribed Image Text:II.
III.
IV.
V.
EINE E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Learning Goal: To understand the ideal gas law and be able to apply it to a wide variety of situations. The absolute temperature T, volume V, and pressure p of a gas sample are related by the ideal gas law, which states that pV nRT. Here is the number of moles in the gas sample and R is a gas constant that applies to all gases. This empirical law describes gases well only if they are sufficiently dilute and at a sufficiently high temperature that they are not on the verge of condensing. In applying the ideal gas law, p must be the absolute pressure, measured with respect to vacuum and not with respect to atmospheric pressure, and T must be the absolute temperature, measured in kelvins (that is, with respect to absolute zero, defined throughout this tutorial as -273°C). If p is in pascals and Vis in cubic meters, use R 8.3145 J/(mol-K). If p is in atmospheres and V is in liters, use R = 0.08206 L-atm/(mol-K) instead. Part A A gas sample enclosed in a rigid metal container at room…arrow_forwardA gas thermometer registers an absolute pressure of 305 mm of mercury when in contact with water at the triple point. What pressure does it read when in contact with water at the normal boiling point?arrow_forwardHow can the equation of the diffusion coefficient be expressed in terms of the Boltzmann constant now in terms of R and N (gas constant and number of Avogadro, respectively).arrow_forward
- The figure below shows a gas contained in a vertical piston–cylinder assembly. A vertical shaft whose cross-sectional area is 0.8 cm2 is attached to the top of the piston. Determine the magnitude, F, of the force acting on the shaft, in N, required if the gas pressure is 3 bar. The masses of the piston and attached shaft are 24.5 kg and 0.5 kg, respectively. The piston diameter is D = 10 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 1 bar. The piston moves smoothly in the cylinder and g = 9.81 m/s2.arrow_forwardCan you please answer number 3 and show all of the stepsarrow_forwardShow ALL pertinent solutions. Tabulate data of iteration after the solution.arrow_forward
- Some N2 has is mixed with some O2 has and the sketch below shows a representative sample of the mixture. The total pressure of the mixture is measured and found to be 3.00 atm. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas in this mixture. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. You may assume each behave as an ideal gasarrow_forwardThe air quality index in Beijing last year recorded average ozone (O3) levels of 110 ppb (on a mol basis). Does this exceed Canada's acceptable 24 hour National Ambient Air Quality Objective (NAAQO) of 50 micrograms/M3? Assume the average molar mass of air is 29.0 g/mol and its density is 1.225 kg/M3.arrow_forwardA two phase liquid - vapor mixture of refridgerant a2 is Contained in a ciosed tank at 10 bar. The quality is l60% and the mass of saturated liquid is 25 kg. Calculate the volume of saturated vapor in m*. Use 5 signiigant figures.arrow_forward
- A cell doesn’t need a circulatory system, but your body does. Let’s do a quick calculation to see why. A typical cell has a diameter of 10 mm. The smallest mammals in the world, shrews, are about 10 μm across. Compute the diffusion time for oxygen molecules through water at 25°C for these two distances.arrow_forwardThe mean free path of a gas at a temperature T1 and a pressure P1 is 7x10-5 cm. At these temperature and pressure, there are 2x1018 molecules/cm³. Use results from kinetic theory to determine the collision diameter, o. 4.01 Angstrom 5.01 Angstrom 6.01 Angstrom 7.01 Angstromarrow_forwardPlease and thank you! Make sure the answer is in the correct units!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios