
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Give every answer of all questions and take like
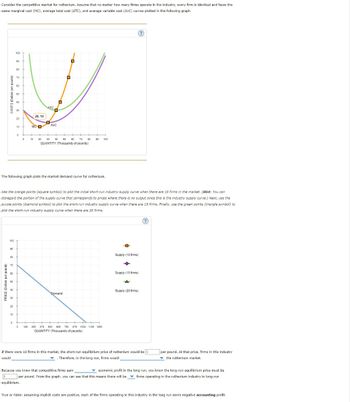
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the competitive market for ruthenium. Assume that no matter how many firms operate in the industry, every firm is identical and faces the
same marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves plotted in the following graph.
COSTS (Dollars per pound)
100
90
80
20, 10
20
ATC
AVC
10
MC
0
0
10
20
40
50 80 70 80
00
100
QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds)
The following graph plots the market demand curve for ruthenium.
Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the initial short-run industry supply curve when there are 10 firms in the market. (Hint: You can
disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the
purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 15 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to
plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms.
PRICE (Dolars per pound)
100
90
80
70
Supply (10 firms)
Supply (15 firms)
40
Supply (20 firms)
Demand
20
10
0
0
125
250
375 500 625 750 875 1000 1125 1250
QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds)
If there were 10 firms in this market, the short-run equilibrium price of ruthenium would be $
. Therefore, in the long run, firms would
would
Because you know that competitive firms earn
per pound. At that price, firms in this industry
the ruthenium market.
economic profit in the long run, you know the long-run equilibrium price must be
per pound. From the graph, you can see that this means there will be firms operating in the ruthenium industry in long-run
equilibrium.
True or False: Assuming implicit costs are positive, each of the firms operating in this industry in the long run earns negative accounting profit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- difference between goods and services?arrow_forwardTrying to figure out?arrow_forwardSuppose you go to a restaurant and buy an expensive meal. Halfway through, despite feeling quite full, you decide to clean your plate. After all, you think, you paid for the meal, so you are going to eat all of it. What’s wrong with this thinking?arrow_forward
- Answer this questionarrow_forwardDoes only making money advance the automobile’s goals or are there perhaps additional reasons that you can name and discuss in detail.arrow_forwardWhat examples do you have of goods or services that are both consumer goods and resources depending upon the context in which those goods are used?arrow_forward
- economic factors thst affect healthy eatingarrow_forwardEconomics A person likes to gamble and has $100 on him. He is going to play the following game: if he bets $b, then with probability p, 0 < p< 1, he will win $b; with probability 1 – p, he will lose his $b. He is given the opportunity to play at most 20 times. He is a very disciplined gambler and is going to use the following strategy: • Every time he plays, he will make a bet equal to half of the amount of money he has at that moment. • If the amount of money he has gets to $300 or higher, then he will stop playing. Find the probability that, starting with $100 and given 20 chances to play the game, this person will get to $300 or more. Formulate this problem recursively by writing down the “Bellman equation." What is (are) the state variable(s)? Be specific about any constraints or initial/boundary conditions for this problem.arrow_forwardDiscuss the principles of individual decision making with examplesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education