Question
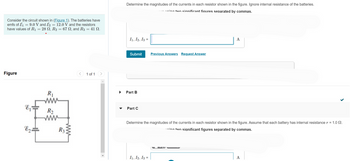
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the circuit shown in (Figure 1). The batteries have
emfs of E₁ = 9.0 V and E2 = 12.0 V and the resistors
have values of R₁ = 28 N, R₂ = 67 N, and R3 = 41 n.
Figure
E₁
E2.
R₁
R2
www
R3
1 of 1
Determine the magnitudes of the currents in each resistor shown in the figure. Ignore internal resistance of the batteries.
using two significant figures separated by commas.
I1, I2, I3 =
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
Part B
Part C
A
Determine the magnitudes of the currents in each resistor shown in the figure. Assume that each battery has internal resistance r = 1.0.
eing two significant figures separated by commas.
I₁, I2, I3 =
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The resistor network in the diagram has 12.0 V across its end terminals labeled A and B. 1kf 2k12 1kf2 wwwwwww www 4k02 What is the current through the 2.0 k2 resistor? Express your answer to the nearest mA.arrow_forwardThree resistors with values 1.8 Ω, 2.6 Ω, and 4.2 Ω are connected in parallel in a circuit with a 7.8 V battery. Part A What is the total equivalent resistance? Express your answer using two significant figures. Part B What is the voltage across each resistor? Express your answer using two significant figures. Part C What is the power delivered to the 4.2 Ω resistor? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardGiven a gold wire and a silver wire that are each 60.0 cm long and have a diameter of 2.00 mm, determine the equivalent resistance of the combination when they are joined together as shown in the diagram. The resistance is to be measured between the free ends A and B. 40.0 cm A Gold wire Silver wire Barrow_forward
- The resistors in the circuit below have the following values: R, = 8.10 N, R, = 7.00 N, and R, = 3.50 N. The two batteries each have a voltage of 3.00 V. R2 R1 R3 (a) Find the current in through R2. A (b) How much power do the batteries deliver to R,? W wwarrow_forwardFind the currents (in A) flowing in the circuit in the figure (indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Due to the nature of this problem do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculationsarrow_forwardHow to solve this questionarrow_forward
- In the circuit illustrated in the figure, obtain the magnitude and direction of the current through each resistor and the potential drop knowing that R1 and R4 = 40, R2 and R5 = 60, R6 = 8Q, R3 and R7 = 60. V1=6V and V2=12V. R3 R₁ R5 Viem,2 RA Write every calculus step by step, completely. All procedure. R₂ V fem,1 R7 ww R6arrow_forwardWhat is the resistance of Part A A 1.1-m-long gold wire that is 0.50 mm in diameter? Express your answer in ohms. ινα ΑΣφ ? R = Ω Submit Request Answer Part B A 80-cm-long piece of carbon with a 1.0 mm x 1.0 mm square cross section? Express your answer in ohms. ? R = Ω Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardThree resistors are connected as shown below. R1 = 25 Ω, R2 = 35 Ω, and R3 = 28 Ω. The voltage across the battery is 90 V. What is the current through R3, in Amperes? Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forward
- You charge an initially uncharged 63.1 mF capacitor through a 21.9 Q resistor by means of a 9.00 V battery having negligible internal resistance. Find the time constant r of the circuit. What is the charge Q on the capacitor 2.01 time constants after the circuit is closed? Q = C What is the charge Q, after a long amount of time has passed? Oo = Carrow_forwardIn the figure the current in resistance 6 is i6 = 1.39 A and the resistances are R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 2.390, R4 = 14.30, R₂ = 7.70 Q, and R₂ = 4.26 Q. What is the emf of the ideal battery? Number i E R₁ Units R3 www R₂ R₁ www R₂ R₁arrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in (Figure 1). The batteries have emfs of E1=9.0V and E2=12.0V and the resistors have values of R1=28Ω, R2=68Ω, and R3=34Ω. A) Determine the magnitudes of the currents in each resistor shown in the figure. Ignore internal resistance of the batteries. B) Determine the directions of the currents in each resistor. Ignore internal resistance of the batteries. a) I1 right, I2 left, I3 up b) I1 left, I2 right, I3 down c) I1 left, I2 right, I3 up d) I1 right, I2 left, I3 downarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios