
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
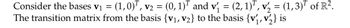
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the bases v₁ = (1,0)¹, v₂ = (0, 1) and v₁ = (2, 1), v₂ = (1,3)¹ of R².
The transition matrix from the basis {V₁, V₂} to the basis {v₁, v₂} is
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Let B = {(1, 3), (-2,-2)} and B' = {(-12, 0), (-4,4)} be bases for R2, and let 3 2 40 be the matrix for T: R2 R2 relative to B. 56°F A = (a) Find the transition matrix P from B' to B. P = (b) Use the matrices P and A to find [v] and [T(v)]B, where [v]B = [-5 4]T. [V] B [T(v)]B = (c) Find P-1 and A' (the matrix for T relative to B'). p-1 = 4arrow_forwardCalculate the 2X2 matrix A for which £, (2) ₁ Eo = span { -(3) 5 that is. all e- vectors associated to the e-value à can be written as a real number number times v. } and E₂= span { The first row of A has entries The second row of A has entries } where E = span {v}, λ and andarrow_forwardFind the coordinates of x = {-10, 2, 4} with respect to the basis consisting of u, {1, 3, 2}, u, = {2, 1, 4}, and u; = {1,0, 6}. -arrow_forward
- Help neeee in part a and B thanks in advancearrow_forwardSuppose A is the matrix for T: R3 - R3 relative to the standard basis. Find the diagonal matrix A' for T relative to the basis B'. -2 -1 A = 0 -1 B' = {(-1, 1, 0), (2, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1)} A' =arrow_forwardThe coordinates for the vector v = (1,2,4) relative to the standard basis B = {(1,0,0), (0, 1,0), (0,0,1)} is [v] B = (1,2,4). The coordinates for v relative to the nonstandard basis B' = {(1, 0, -1), (2,1,-1), (-2, 1,4)} is [v]B¹ = (9,−1,3). Find the transition matrix P-1 from B to B' and show that this does change the coordinate of v relative to B to the coordinate of v relative to B'.arrow_forward
- Find the change-of-coordinates matrix from B to the standard basis in R". 8 3 3 B= 7 -3 - 4 8 P8 =arrow_forwardI know the basis converted to orthogonal is {<2, 1, -1, 1>,<11, -12, 5, -5>,<-1, -3, 0, 5>} and that the magnitude of these will be sqrt(7), sqrt(315), sqrt(35) - but I'm not sure how to use these to convert the basis to orthonormal.arrow_forwardExplain how fixing a basis v1, · · , Vn of V associates to a quadratic form a corresponding function in n variables of the form q(x1,· . for a certain symmetric matrix A = (aj). , Xn) = Li=1 aijXiXj, .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning