
In this study, the researcher compared S N 2 and E2
reaction rates for four substrates. Three of the substrates had a second halogen on the b
position in the molecule. This work also compared the behavior of two nucleophiles:
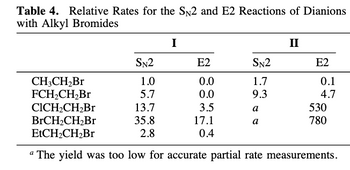
dianion I and II. You should read the abstract and look at Scheme 1 (p. 3082) and Table 4
(p. 3086).
Abstract: The gas-phase reactions of benzoate and phenolate containing dianions with a series of ‚-substituted
alkyl bromides (X-CH2CH2Br, X ) H, F, Cl, Br) have been studied in a quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer.
Branching ratios between SN 2 and E2 products were measured and rate constants were determined. The
‚-halogens increase both the S N 2 and E2 rates, but the effect is greater for the latter process and therefore
these substituents lead to an increase in the amount of elimination. The kinetic data for the SN 2 reactions can
be analyzed via a two-parameter, linear free-energy relationship and the results indicate that field-effects (i.e.,
electron-withdrawing groups) strongly favor the reaction (FF ) 1.83). In contrast, analysis of the available
condensed phase data for these substrates indicates that halogens strongly retard the reaction (FF ) -2.04).
The dramatic reversal in substituent effects can be explained by a simple electrostatic model which suggests
that solvation causes the system to shift to a more highly ionized SN2 transition state.
than EtBr.
4b) Consider Table 4 and suggest why BrCH 2 CH 2 Br (35.8 vs. 5.7) has a higher S N 2 reaction
rate than FCH 2 CH 2 Br.

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

- How would I go about determining the mechanism of this problem?arrow_forwardSTARTING WITH 18MG OF 2-methyl-2-butanol JUST B PLEASE (b) theoretical volume of alkene mixture (ml) expected to be obtained in this experiment.arrow_forwardPlease explain how they are either Sn1, Sn2, E1, or E2.arrow_forward
- Which set of reagents will accomplish this reaction? H3C, O 1. Hz and Pd on barium sulfate (Basoa) in methanol. O 2. Sodium dissolved in liquid ammonia and tert.-butanol. O 3. H2 and Pd-carbon, followed by H30". O 4. Lithium aluminumhydride (LIAIHA) in dry THF,arrow_forward1. 2. CH3 a 1. www 2. CH3 + Br a = Proton transfer b = Lewis acid/base c = Radical chain substitution HCI مار Na benzene, reflux CH₂ d CI d Radical chain addition e = Electrophilic addition f = E1 Elimination 4 HO-CH + NaBr Identify the mechanism by which each of the reactions above proceeds from among the mechanisms listed. Use the letters a - i for your answers. g = E2 Elimination h = SN1 Nucleophilic substitution i = SN2 Nucleophilic substitutionarrow_forwardwhat are the difference between Zaitsev and Hoffman rule. describe their relation with E2 elimination mechanism with some examples.arrow_forward
- solve this problem with mechanisms and showing arrowsarrow_forwardwhat is the purpose of adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a product after distillation? what products would you expect to be produced if H2SO4 were used as the acid catalyst, and an equimolar mixture of NaCl and NaBr were used as the sources of nucleophiles? Based on the previous question: more than one product is actually produced. Will the products be produced in equal amounts. why or why notarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





