
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
- All problems will use the conventional Cartesian coordinate system unless noted otherwise.
- Positive x-axis points to the right,
- Positive y-axis points up,
- Angles are measured CCW (counter-clock-wise) from the positive x-axis.
-
When a numerical input is necessary:
- Enter your answer to 4 significant figures. Use a leading zero for numbers between -1 & 1.
- Do NOT use Scientific Notation.
- Angles must be reported with a minimum of 2 decimal places.
- Report directions as positive angles. For instance, 350 degrees, not -10 degrees.
- Use the "standard" coordinate system unless noted otherwise.
- Regarding the magnitude of an angle between two objects that could be reported with more than one value, submit the smaller value.
- Magnitude shall always be reported as a positive number.
- Value shall be reported either as a positive or negative number based upon the application. When reporting a value, include the sign.
-
Problem-DD:
Consider FIG-DD in the appendix.
Note:
- For Blocks “A” & “B” & “C”:
- The mass of “A” is 30 kg.
- The mass of “B” is 50 kg.
- The mass of “C” is 40 kg.
- Blocks “A” & “B” are in contact.
- Blocks “B” & “C” are in contact.
- Blocks “C” & “inclined plane” are in contact.
- The angle above the horizontal of the inclined plane is Θ = 30°.
- The static coefficients of friction:
- Surface-1: 0.30
- Surface-2: 0.40
- Surface-3: 0.45
- The kinetic coefficients of friction:
- Surface-1: 0.23
- Surface-2: 0.37
- Surface-3: 0.42
FIND:
- Calculate:
- The maximum force of P, such that motion does not occur.
- When this maximum P is applied, determine the remaining forces on the Blocks.
-
NOTE: Surface-3 is the surface between Block-C and the Inclined Plane.
- For Blocks “A” & “B” & “C”:
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 14
Problem-DD
The magnitude of the friction force on Surface-1 is
N.
QUESTION 15
Problem-DD
The magnitude of the normal force on Surface-1 is
N.
QUESTION 16
Problem-DD
The magnitude of the Friction Angle on Surface-2 is
degrees.
QUESTION 17
Problem-DD
The magnitude of the angle between the Normal Force on Surface-2 and a vertical line is
degrees.
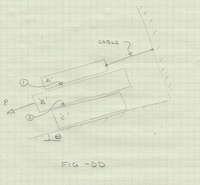
Transcribed Image Text:CABLE
P.
FIG -DD
2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the last step, are we supposed to multiply by 0.5? If so the answer is .65. Is this correct?arrow_forwardA rectangular block of wood is measured to have the dimensions 11.2 cm, 3.4 cm and 4.10 cm. Compute the volume of the block using the rules of significant figures. O 1.645 x 10² cm² a) b) 16 x 10² m² c) 1.6 x 10² cm² d) 1.60x 10² cm² Question 8 (Mandatory) (10 points) Saved 0:21arrow_forwardA rectangle has a length of (5.1 ± 0.2) m and a width of (2.3 ± 0.1) m. Calculate: (a) the area and (b) the perimeter of the rectangle, Give the uncertainty in each value.arrow_forward
- Convert the following measurements to metric units with power-of-ten prefixes. Do not use scientific or engineering notation. Numeric values must range from 1 to less than 1000. Metric prefixes, which are case-sensitive, must be one of the following: M, m, c, k, or µ. (You may use lower-case 'u' in place of 'p'.) Example: 2.00 × 105 m = 200 km Enter the numeric value in the first box, and enter the metric prefix in the second box. a. 3.51 x 10-5 L = b. 7.98 x 108 J = C. -0.000230 W = - W d. 11,200 K = K (note: upper-case 'K' is the abbreviation for the temperature unit 'kelvin')arrow_forwardIn the following calculations, be sure to express the answer in standard scientific notation with the appropriate number of significant figures. 6.477 × 10 m² 4.7036 x 102 m x 10arrow_forwardAn astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, approximately 1.50 × 10° km. The speed of light is about 3.00 x 10° m/s. Express the speed of light in astronomical units per minute. Number Unitsarrow_forward
- il vidong P 7. (10pt) In AABC, ZC = 81°, ZB = 33°, and side c = 15. Find side b of AABC to the nearest tenth. pucg 1701 8. (a) (5pt) Prove the identity: secx-cosx = secx sin²x Ils obulout jollood moitotumnez baicoibai saiwisdio aeslau mmol jalgraiz oszo ni flot bris bolodal (b) (5pt) Find cos, if sin and tan 0 <0 5 snowers odriguia bustolovioc (0.x) mpl ori) to anotulos) airpori y bris x sit state noitsupo ostboup grivollol smil movie (inc E+xxx dgety od dolose or noemolni zid sau no bas tev dr.((,0) bas 9. Find all exact solutions to the trig equations for x = [0, 27): tan(x) = -√3 2 sin(x) = √2 (a) (5pt) (b) (5pt) =-- 10. (a) (5pt) Evaluate the logarithm without using a calculator: log, (819) hoitoup oils bri (b) (5pt) Solve for x and round the answer to the nearest tenth: 12* = 384 110 auibet bos.odnos odi vinobl mol bisbraste 20180b7009 diw storio edino ziniog spot fods. I npitori xalqinos oli vulgrai? woled invig oloro od to noisups silloi odi gniau slonio odi dgers bi 01-…arrow_forwardPlz give correct solution only. The amount of water in reservoirs is often measured in acre-ft. One acre-ft is a volume that covers an area of one acre to a depth of one foot. An acre is 43,560 ft2. Find the volume in SI units of a reservoir containing 75.0 acre-ft of water.arrow_forwardPlease solve the followingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON