
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider a 160-mm-long segment of a simply supported beam. The internal bending moments on the left and right sides of the segment are 60 kN-m and 64 kN-m, respectively. The cross-sectional dimensions of the flanged shape are shown in the accompanying figure. Assume b1 = 180 mm, b2 = 45 mm, b3 = 305 mm, d1 = 70 mm, d2 = 245 mm, d3 = 70 mm. Determine the maximum horizontal shear stress in this segment of the beam.
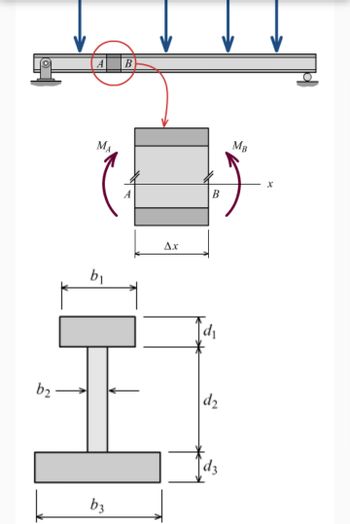
Transcribed Image Text:b₂
M₁
b₁
b3
B
A
Δε
d
B
d₂
MB
Х
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a 175-mm-long segment of a simply supported beam. The internal bending moments on the left and right sides of the segment are 75 kN-m and 80 kN-m, respectively. The cross-sectional dimensions of the flanged shape are shown in the accompanying figure. Assume b1 = 120 mm, b2 = 50 mm, b3 = 210 mm, d1 = 75 mm, d2 = 175 mm, d3 = 75 mm. Determine the maximum horizontal shear stress in this segment of the beam.arrow_forward2. A two-member truss structure is loaded as shown. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the displacement of point A. CY dimensions in meters TAB 3 A 80KN 4:5 EAB 70 GPa ; EAC=70 GPa AAB=150mm²; AAC = 100mm²arrow_forwardConsider a 125-mm-long segment of a simply supported beam. The internal bending moments on the left and right sides of the segment are 60 kN-m and 68 kN-m, respectively. The cross-sectional dimensions of the flanged shape are shown in the accompanying figure. Assume b1 = 160 mm, b2 = 30 mm, b3 = 255 mm, d1 = 75 mm, d2 = 220 mm, d3 = 75 mm. Determine the maximum horizontal shear stress in this segment of the beam.arrow_forward
- Using either the Portal Method or Cantilever Method, determine all the member forces of the frame shown below. Submit your answers in the format where the member forces are written along the corresponding members as illustrated in the short video discussion. Computation of such values may no longer be shown. a= 7 m b= 9 m P= 113 KN 3P/2 P G a H E b I F с 4m 5marrow_forwardSolve the problem by the moment-area method. The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P at the positions shown in the figure. B C 4. 4 A support C at the midpoint of the beam is positioned at distance d below the beam before the loads are applied. Assuming that d = 12 mm, L = 5.4 m, E = 200 GPa, and I = 193 x 10° mm, calculate the magnitude of the loads P (in kN) so that the beam just touches the support at C. 163.87 x kNarrow_forwardConsider a 200-mm-long segment of a simply supported beam. The internal bending moments on the left and right sides of the segment are 70 kN-m and 74 kN-m, respectively. The cross-sectional dimensions of the flanged shape are shown in the accompanying figure. Assume bq = 155 mm, b2 = 30 mm, b3 = 245 mm, d1 = 65 mm, d2= 200 mm, d3 = 65 mm. Determine the maximum horizontal shear stress in this segment of the beam. b1 b2 d2 MA MB |dz A B b3 Ax Answer: Tmax = i MPaarrow_forward
- A beam is subjected to equal bending moments of M₂ = 4300 N·m. The cross-sectional dimensions are b = 120 mm, c = 33 mm, d = 67 mm, and t = 4 mm. Determine: (a) the centroid location (measured with respect to the bottom of the cross-section), the moment of inertia about the z axis, and the controlling section modulus about the z axis. (b) the bending stress at point H. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (c) the bending stress at point K. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (d) the maximum bending stress produced in the cross section. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. Answer: (a) y= i mm M 1₂ = i mm4 S= mm³ (b) OH = i MPa (c) OK = i MPa (d) gmax= i MPa (typ) b H Karrow_forwardCalculate for the shear force in kN at member ED of the frame shown in figure 1 using Portal Method. Enter absolute value and use 2 decimal places in your solution.arrow_forwardThe cantilever beam shown in Figure A is subjected to load magnitudes of Pz = 3.0 kips and Py = 8.1 kips. The flanged cross section shown in Figure B has dimensions of bf = 7.1 in., tf = 0.55 in., d = 11.5 in., and t = 0.35 in. Using L = 70 in., determine: (a) the bending stress at point A. (b) the bending stress at point B. (c) the angle for the orientation of the neutral axis relative to the +z axis. Note that positive angles rotate clockwise from the+z axis. FIGURE A P₂ L B tw bf D FIGURE Barrow_forward
- For the forces acting on the beam shown in Figure 3.1h, determine the location of the equivalent resultant force with reference to point A in m. Givenl= 2.4, P1 = 45, P2 = 90, w1= 40 and w2 = 60. (Note: Prefix the value with negative sign "-" if the location is to the left of the reference point. E.g. if the location of the equivalent resultant is located between points A and B, or to the left of point B by 1.2m, the answer should be "-1.2" with reference to point B) P, kN P2 kN W, kN/m W, kN/m C Im 21 m 21 m Figure 3.1harrow_forwardConsider a 150-mm-long segment of a simply supported beam. The internal bending moments on the left and right sides of the segment are 70 kN-m and 76 kN-m, respectively. The cross-sectional dimensions of the flanged shape are shown in the accompanying figure. Assume b1 = 155 mm, b2 = 30 mm, b3 = 265 mm, d1 = 65 mm, d2 = 220 mm, d3 = 65 mm. Determine the maximum horizontal shear stress in this segment of the beam.arrow_forwardConsider a 110-mm-long segment of a simply supported beam. The internal bending moments on the left and right sides of the segment are 55 kN-m and 61 kN-m, respectively. The cross-sectional dimensions of the flanged shape are shown in the accompanying figure. Assume b1 = 165 mm, b2 = 45 mm, b3 = 265 mm, d1 = 65 mm, d2 = 240 mm, d3 = 65 mm. Determine the maximum horizontal shear stress in this segment of the beam.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning