
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Solve first two parts only
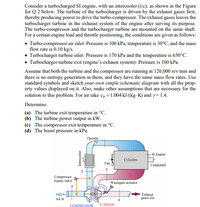
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a turbocharged SI engine, with an intercooler (i/c), as shown in the Figure
for Q 2 below. The turbine of the turbocharger is driven by the exhaust gases first,
thereby producing power to drive the turbo-compressor. The exhaust gases leaves the
turbocharger turbine in the exhaust system of the engine after serving its purpose.
The turbo-compressor and the turbocharger turbine are mounted on the same shaft.
For a certain engine load and throttle positioning, the conditions are given as follows:
• Turbo-compressor air inlet: Pressure is 100 kPa, temperature is 30°C, and the mass
flow rate is 0.10 kg/s.
• Turbocharger turbine inlet: Pressure is 170 kPa and the temperature is 650°C.
• Turbocharger turbine exit (engine's exhaust system): Pressure is 100 kPa.
Assume that both the turbine and the compressor are running at 120,000 rev/min and
there is no entropy generation in them, and they have the same mass flow rates. Use
standard symbols and sketch your own simple schematic diagram with all the prop-
erty values displayed on it. Also, make other assumptions that are necessary for the
solution to this problem. For air take c, =1.004 kJ/(kg-K) and y= 1.4.
Determine:
(a) The turbine exit temperature in °C.
(b) The turbine power output in kW.
(c) The compressor exit temperature in °C.
(d) The boost pressure in kPa.
Throttle
SI Engine
Cylinders
Fan
Crankshaft
2
Compressor
bypass valve
Wastegate actuator
Exhaust
Air in
gases out
COMPRESSOR
TURBINE
Intercooler
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY